We offer advanced design and quality synthesis for predesigned siRNA and siRNA libraries using the Rosetta siRNA Design Algorithm to reduce offtarget effects and increase RNAi performance The algorithm utilizes PositionSpecific Scoring Matrices (PSSM) and knowledge of the siRNA seed region to predict the most effective and specific siRNAThe siRNA Nonseed Region and Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants of OffTarget Effects PLoS Comput Biol 15 Dec 11;11(12)e doi /journalpcbi eCollection 15 Dec Authors Piotr J Kamola 1 Several recent studies suggest that the main source of siRNAmediated offtarget gene silencing could be the complementation between the 'seed' region of
Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics
Seed region sirna
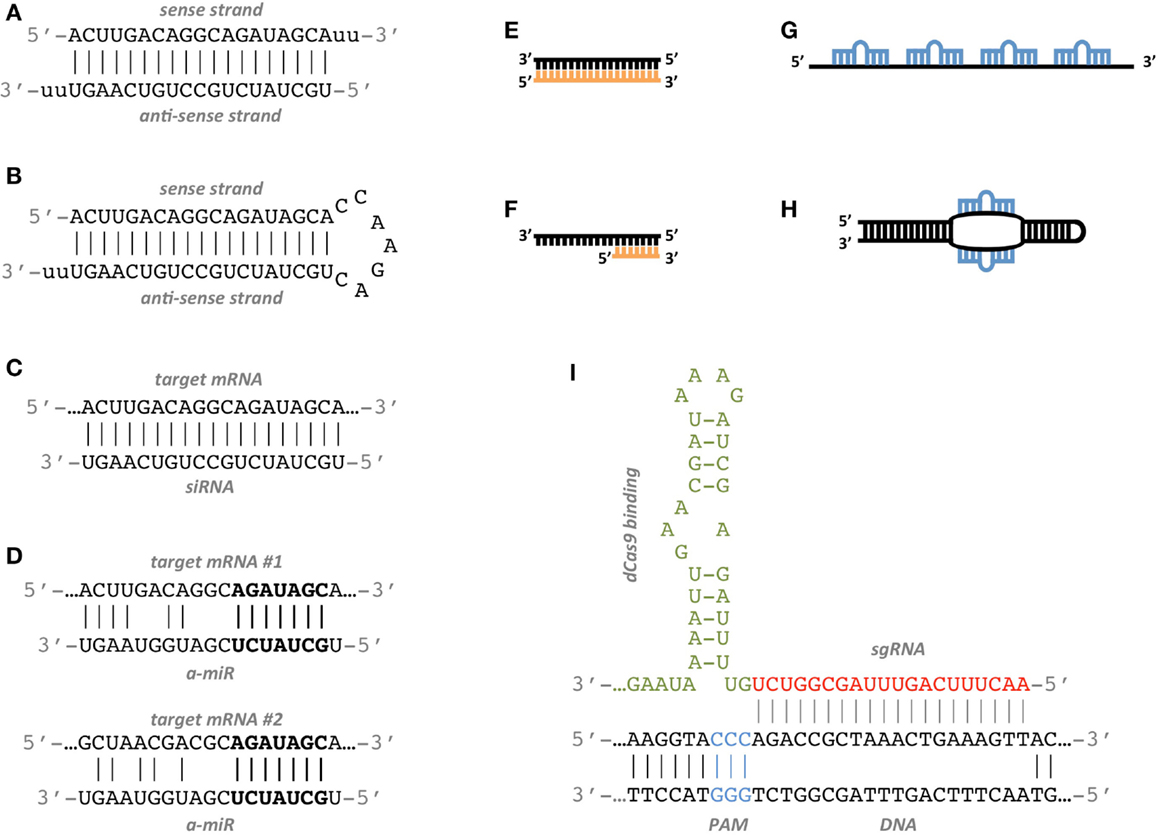
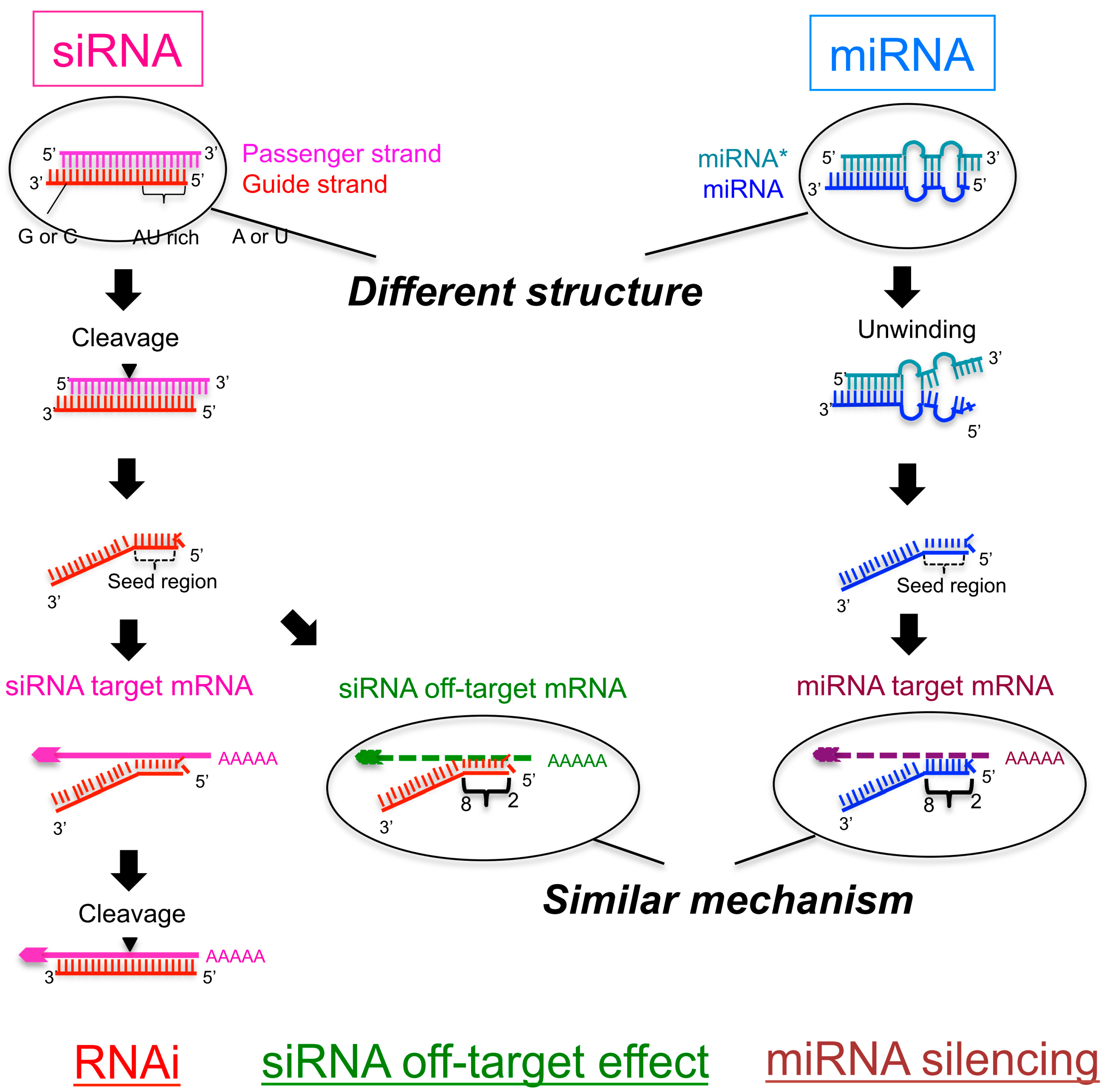
Seed region sirna-SiRNA is designed to be perfectly complementary to the target mRNA and, miRNA follows the "seed pairing rule", a complementary binding of miRNA seed region to binding site (BS) located in the mRNA 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) (Figure 1C) The seed region involves nt 28 from miRNA 5' end or possibly nt 27 and 26So, we have looked for the rules that govern the capability of siRNAs to induce seeddependent offtarget effect, and revealed that the efficiency of offtarget effect is highly correlated to the thermodynamic stability of the duplex formed between the seed region of siRNA guide strand and its target mRNA (UiTei et al, 08)




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram
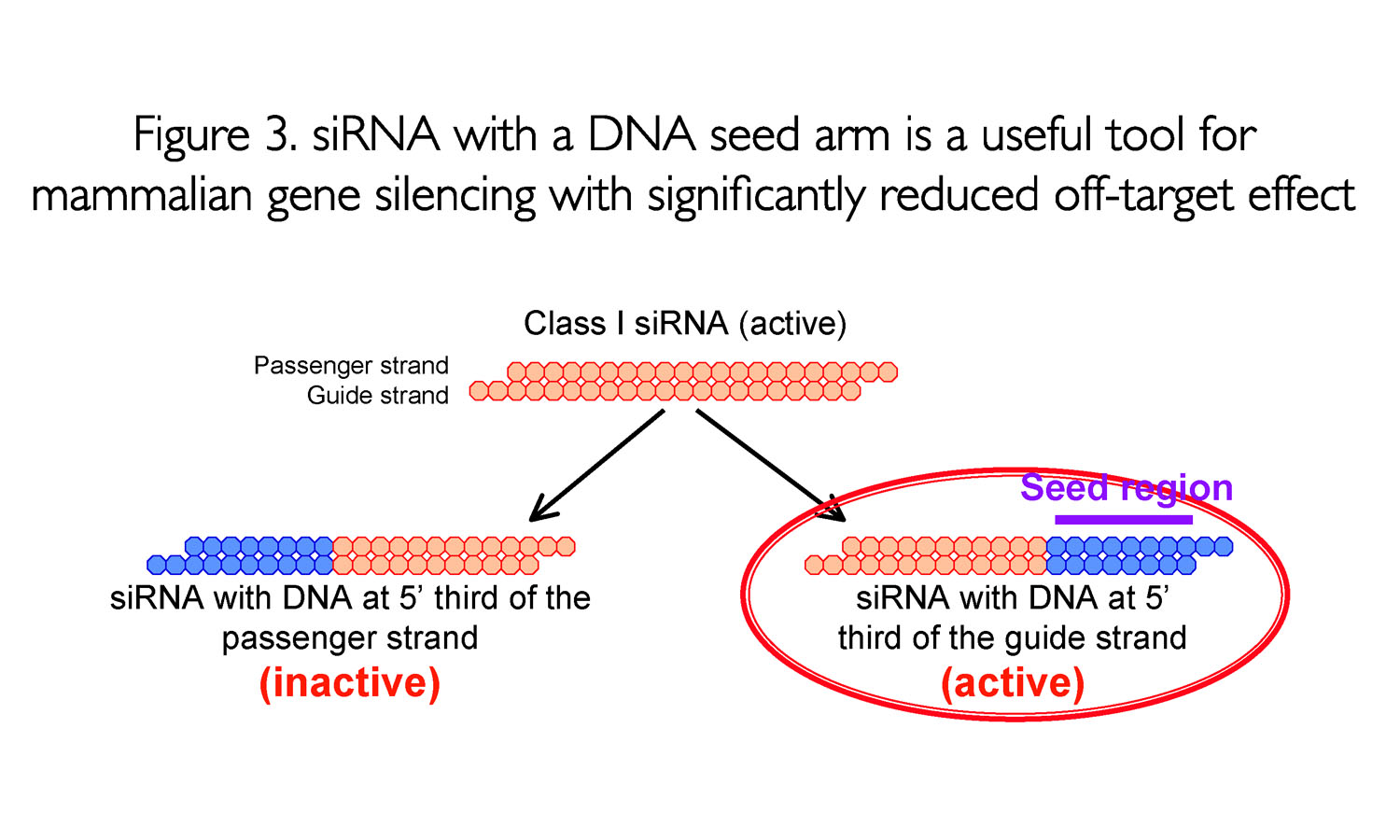
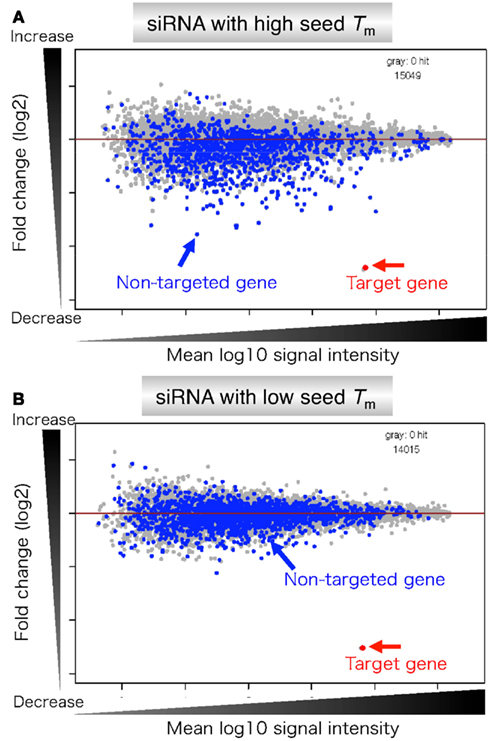
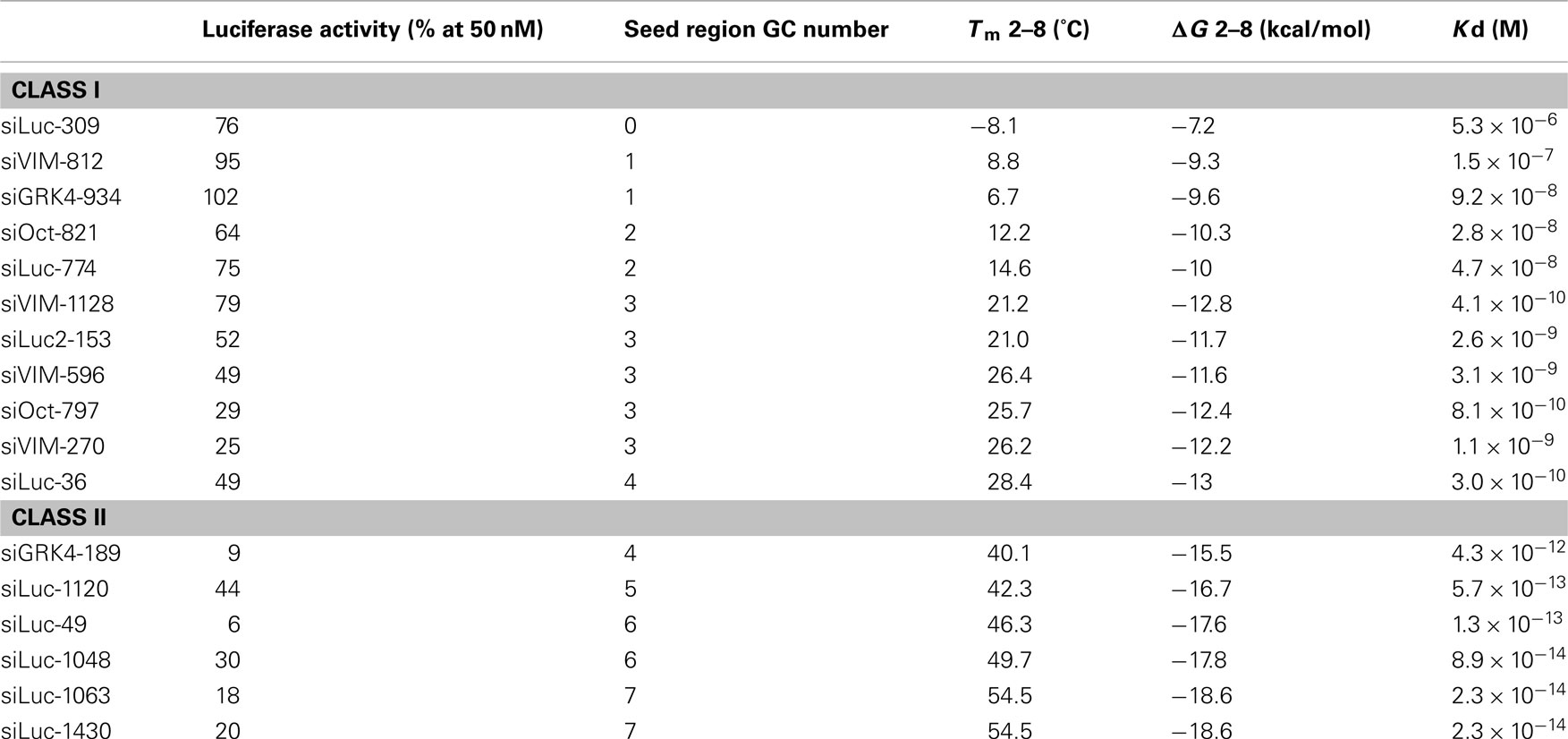
A highly functional siRNA may consist of two regions, the seed duplex region, which is capable of being totally replaced with DNA without substantial loss of gene silencing activity, and the nonseedduplex region, most of which should be RNA and possibly provide binding sites for RNAbinding RLC/RISC proteinsThe seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence" has to be perfectly complementaryThe results revealed that the seeddependent offtarget efficiency was positively and negatively correlated with the melting temperature (T m) (r = 074, Figure 2a) and standard free energy change (Δ G) (r = −069), respectively, calculated by the nearestneighbor procedure for the formation of the duplex between the siRNA seed region
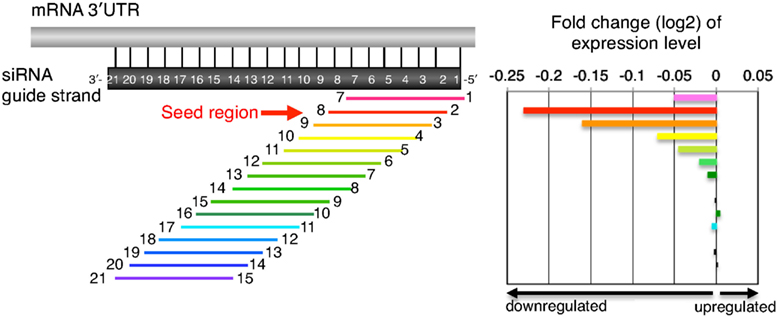
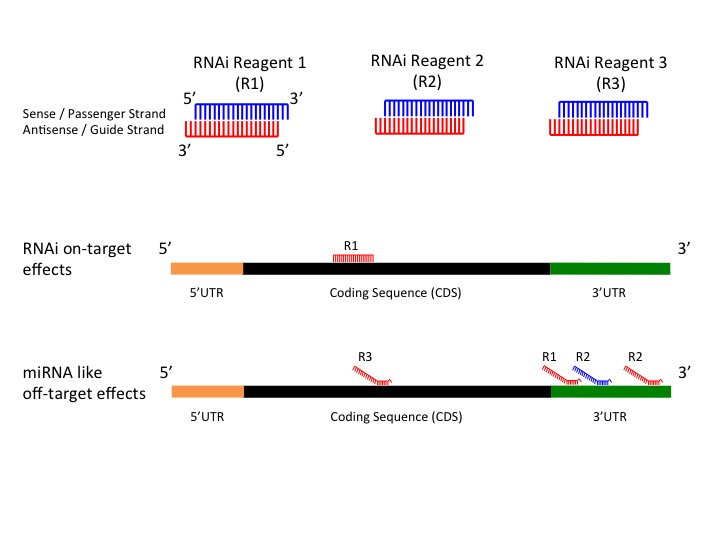
The primary source of siRNAmediated offtargets is the seed region (nucleotides 27), which uses the microRNA pathway to induce nonspecific gene silencing via interactions within the 3' UTR Incorporating comprehensive bioinformatic strategies such as seed region filters and seed frequency analysis within the SMARTselection design strategyScripts with complementarity to the seed region of the siRNA antisense strand When compared to 2amethoxy ribosyl (2aOMe) modified siRNAs previously developed to alleviate antisense offtarget silencing;SiRNA screens is likely due to offtarget effects8 siRNA offtarget effects have been linked to the mechanism of action for miRNAs, 9 in which a short sequence on the 5′ end of the RNAi duplex (the "seed region," bases 2–8) is complementary to the 3′UTRs of multiple mRNAs, causing degradation of their associated transcripts7,10 Because
Allows you to choose the region the siRNA targets (5' or 3' UTR or ORF), G/C percentage, and if you want to BLAST search the sequence Naito et al siDirect Identifies siRNA targets based on nucleotide sequence Provides location within the sequence, melting temperature of seed duplex, and a minimum number of mismatches against offtarget Clearly, the seed sequences of miRNA (identified with miRNA databases) should be avoided in siRNA design 69 In addition, the siRNA should have a low thermodynamic stability of the duplex between the seed region of the guide strand of siRNA and its target mRNA, since a low seedtarget duplex stability reduces the capability of siRNA to induce The siRNA having minimum T m value of seed target duplex, no offtarget for the overall guide strand (including both seed as well as nonseed regions) and least number of offtargets for the passenger strand was considered best 14 To confirm null guide strand offtarget effect, the region of leader sequence targeted by best siRNA was evaluated



Whole Genome Thermodynamic Analysis Reduces Sirna Off Target Effects




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal
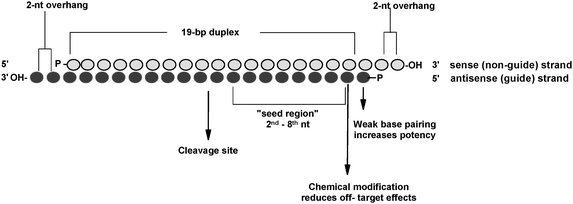
Key words RNAi, siRNA, Seed region, Offtarget effect, OMe 1 Introduction RNA interference (RNAi) is induced by small interfering RNA (siRNA), a duplex composed of the guide and passenger strands of 21nucleotide (nt)long RNAs with 2nt 30 overhangs The siRNA is loaded onto Argonaute (AGO) protein, which is a core As the offtarget effects were identified based on perfect complementarity to the seed region (positions 2–8) and both terminal nucleotides of siRNA are known to be incorporated into Ago protein (positions 1 and 21), the potential basepairing between siRNA and offtarget mRNA was determined via positions 9– (ie 3' region) The number SiRNA is designed to be perfectly complementary to the target mRNA and, miRNA follows the "seedpairing rule", a complementary binding of miRNA seed region to binding site (BS) located in the mRNA 3' untranslated region (3'UTR) (Figure (Figure1C) 1 C) The seed region involves nt 28 from miRNA 5' end or possibly nt 27 and 26



Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife



1
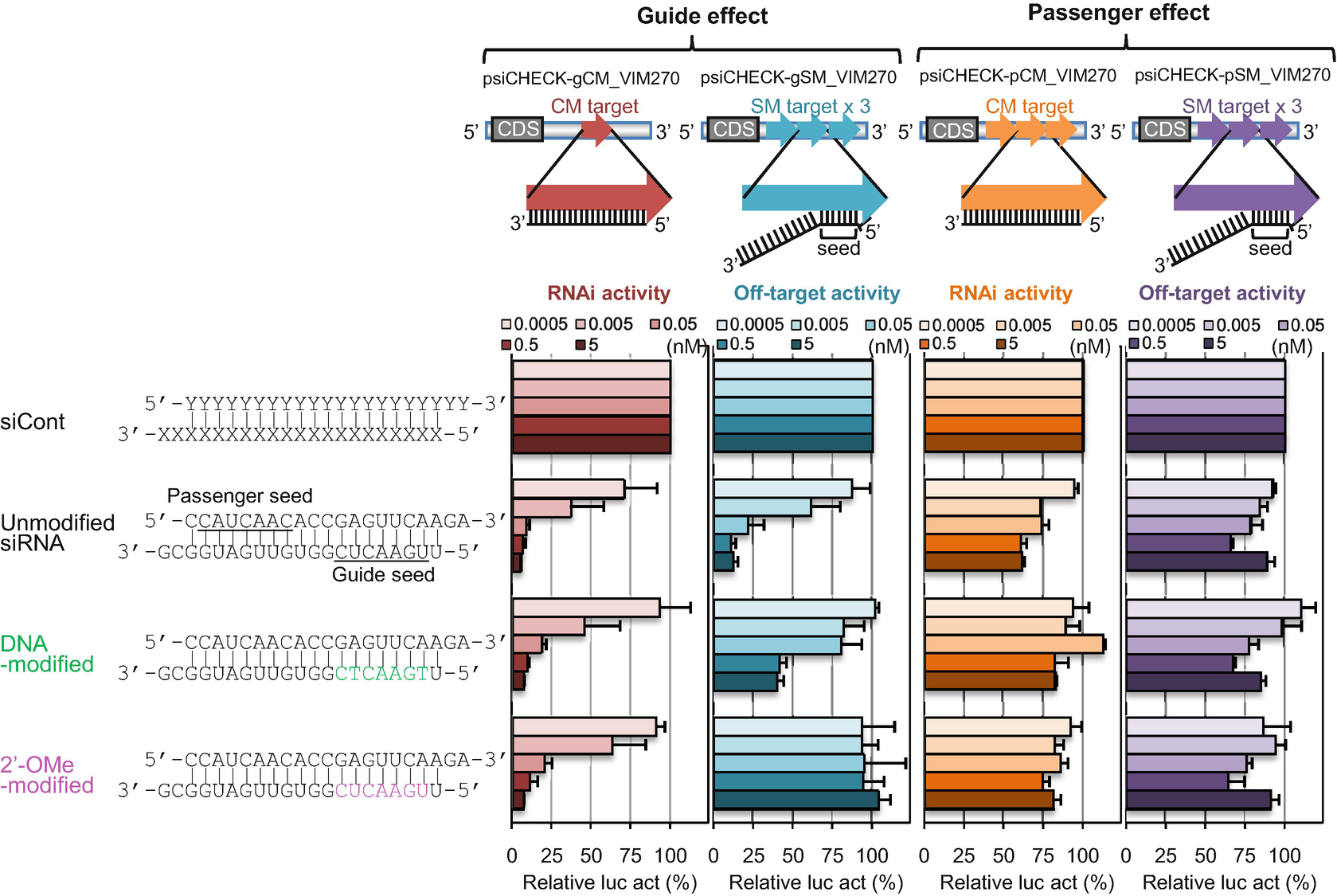
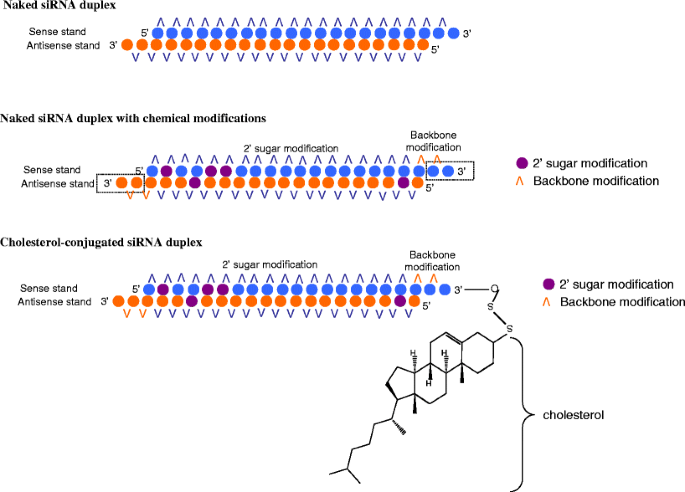
Chemical modifications of 2′Omethyl (2′OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 2–8) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA with 2′OMe modifications inhibited the expression of a completelymatched (CM) target gene, whereas that with LNA modifications didThe bulge modification could better discriminate between on versus offtargets Our results suggest that the bulgeSmartBase TM siRNA Recommended Modifications 1 Alternating 2'F bases and 2'OMe bases in siRNA enhances duplex stability and are more resistant to RNase degradation 2 Use a few 2'OMe bases in the seed region of the guide strand to decrease the Tm below 215 of this region 2'O methyl base hybridization with RNA has a lower TM



1



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics
Asymmetric replacement of seed region nucleotides with DNA bases has also been shown to reduce offtargeting as a result of seed region complementarity within the passenger strand Recent in vitro studies have shown that shRNA produces fewer offtarget effects than siRNACompared with an siRNAlike approach, the requirement of perfect complementarity of the microRNA seed region to a given target sequence in the microRNA/target model has proven to be a more efficient strategy, accomplishing the selective targeting ofNew bioinformatics techniques to decipher real positives from false positives that arise from the seed region have been highlighted in this publication Seed sequencedriven offtarget effects have been extensively observed in siRNAs screens as they stem from the endogenous miRNA mechanism of seeddriven mRNA regulation



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics




Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text
Chemical modifications of 2'Omethyl (2'OMe) and locked nucleic acid (LNA) of the nucleotides in the seed region (positions 28) of the small interfering RNA (siRNA) guide strand significantly reduced seedmatched (SM) offtarget effects The siRNA with 2'Seed region The chemical modifications of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), PS, and DNA−PS were introduced into all of the seven nucleotides of the seed region of the siRNA guide strand (Figure 2b) In addition, 3 (positions 4−6), 5 (positions 3−7), and 7 (seed(A) Sequences complementary to the RMRPderived endosiRNA, with or without mutations in the seed region alone (seed) or the seed region and nucleotides 12–15 (seed/12–15), were inserted into the psiCHECK2 vector HeLa, 293T and MCF7 cells were transfected with the vectors and luciferase activity was measured 48 h posttransfection




Abundant Expression Of Maternal Sirnas Is A Conserved Feature Of Seed Development Pnas




Signature Transcript 39 Utrs Contain Sequence Complementarity To Sirna Download Scientific Diagram
Every backbone phosphate of the seed nucleotides at positions 2–8 from the anchored 5′terminal nucleotide preordered on the AGO protein to make stable basepairing between the siRNA seed region and target mRNA in an Aform helix 11,12 The efficiency of the offtarget effect is positively correlated with the thermodynamic stability of theKeywords RNAi, Offtarget effects, Data analysis, Seed region, miRNA, siRNA, shRNA, Highthroughput screening Background RNA interference (RNAi) is a posttranscriptional gene regulatory mechanism 1 that has been widely used for functional genomics studies both in cell lines and organisms The synthetic duplexes referred to as small interTo avoid off target effect, siRNA Wizard filter candidate siRNA sequence to remove sequence displaying a known miRNA SEED recognition region at 3' end Loop for short hairpin siRNAs (shRNA) We and others have tested a variety of sequences for the loop between the two complementary regions of a shRNA, ranging from 3 to 9 nt in length




Sidesign Center User Guide




Sirnas And Shrnas Tools For Protein Knockdown By Gene Silencing
The seed region comprises 6 nucleotides in positions 2–7 of the antisense siRNA strand of the siRNA duplex Matches such as these can contribute to downregulation of unintended targets due to the siRNA mimicking the action of an miRNA siRNA designed at QIAGEN is analyzed for 3' UTR/seed region complementarity using a proprietary set of 3The Rosetta siRNA Design Algorithm utilizes PositionSpecific Scoring Matrices and knowledge of the seed region to predict the most specific and effective sequences for your target genes The algorithm's rules were developed utilizing empirical data collected from gene silencing experiments carried out over three yearsKeywords RNAi, Offtarget effects, Data analysis, Seed region, miRNA, siRNA, shRNA, Highthroughput screening Background RNA interference (RNAi) is a posttranscriptional gene regulatory mechanism 1 that has been widely used for functional genomics studies both in cell lines and organisms The synthetic duplexes referred to as small inter




Nanomedicines Based On Recombinant Fusion Proteins For Targeting Therapeutic Sirna Oligonucleotides Therapeutic Delivery



Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink
Minimization of seeddependent offtarget effects siDirect selects siRNAs with lower Tm value at the seed region, which contains 7 nucleotides at positions 28 from 5′ end of the guide strand siRNAs downregulate many unintended genes whose transcripts have complementarities to the siRNA seed regionSmall interfering RNA (siRNA), sometimes known as short interfering RNA or silencing RNA, is a class of doublestranded RNA noncoding RNA molecules, typically 24 base pairs in length, similar to miRNA, and operating within the RNA interference (RNAi) pathway It interferes with the expression of specific genes with complementary nucleotide sequences by degrading mRNA Alternatively, siRNA could cause "partial offtarget" (seed matching offtarget) effects, in cases where the designed siRNA seeding region (second to seventh position) matches with 3′UTR of offtarget, affecting its translation This homology based offtarget could affect siRNA potency as they become unavailable to bind with the intended




Many Si Shrnas Can Kill Cancer Cells By Targeting Multiple Survival Genes Through An Off Target Mechanism Elife




A The Structure Of Sirna Sense And Antisense Strands And Target Mrna Download Scientific Diagram
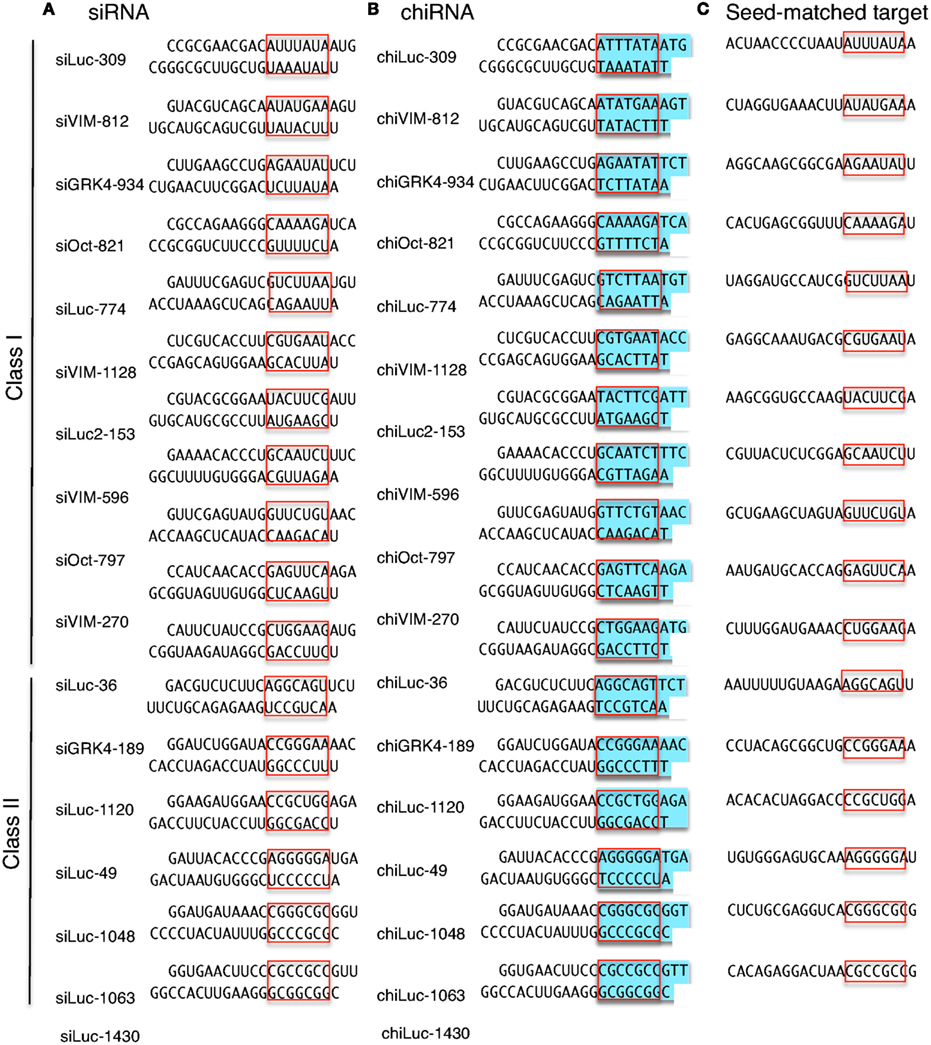
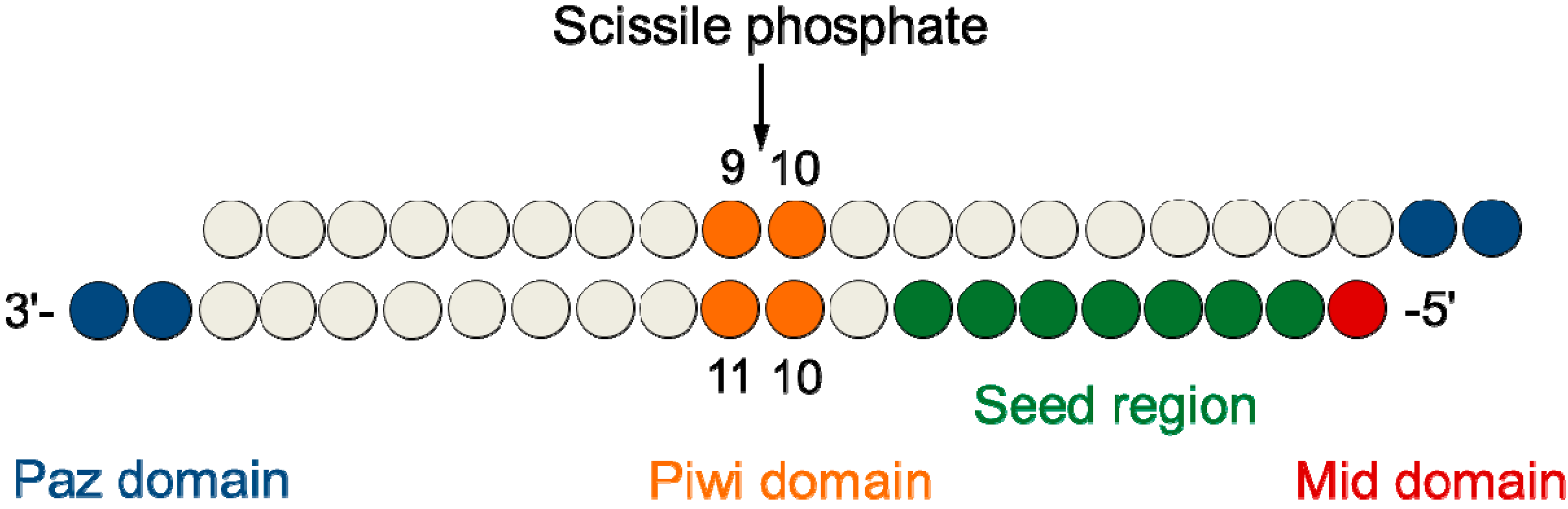
For examination of offtarget effects resulting from the seed region of the siRNA sequences, three mutated siRNA sequences were designed in which individual point mutations were introduced into positions 1, 4, and 14, respectively, of the siRNA strand corresponding to Applied Biosystems siRNA (CLIC2 sequence C) In each case, the siRNAThe seed region of siRNA guide strand and target mRNA (seedtarget duplex) (Figure 1a) 12 Furthermore, we have developed a DNARNA chimeric siRNA (chiRNA) with deoxyribonucleotides in the 5' proximal eight nucleotides of the guide strand and the complementary nucleotides The chiRNA showed virtually no offtarget effects, siRNA recognition of the target mRNA is conferred by the "seed region", a six nucleotide stretch corresponding to positions 27 on the antisense siRNA strand After the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated



Biological And Physicochemical Characterization Of Sirnas Modified With 2 2 Difluoro 2 Deoxycytidine Gemcitabine New Journal Of Chemistry Rsc Publishing



Rnai For Treating Hepatitis B Viral Infection Springerlink
The nonseed region of siRNA was found to be subdivided into four domains, in which two nucleotide pairs (positions 13 and 14) were replaceable with cognate deoxyribonucleotides without reducing RNAi activity However, RNA sequences at positions 912 and 1518 were essential for effective gene silencing, RESULTS In a separate study, we showed that siRNAs can silence unintended transcripts with sequence complementarity to seed regions of siRNAs (Jackson et al 06)Furthermore, we showed that base substitutions in the siRNA seed region disrupt regulation of unintended transcripts, just as mismatches disrupt miRNA target regulation (Doench and The stability between seed region and target mRNA is a determinant of the efficacy of siRNA offtarget effects 33 Thus, the high stability of the seed




Frontiers Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Genetics



Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo
Seed region analysis determines the number of exact matches of the siRNA seed region (nucleotides 27) to the 3'UTRs of all genes in the chosen genome (only performed for human, mouse, and rat) siRNAs with low seed region frequency will have reduced likelihood of seedregion mediated offtarget effects compared to those with higher frequencies1Size of seed region of siRNA we proposed is 68 bases Functional alignment Besides general sequence alignment, GenScript siRNA design tool incorporates a novel alignment approach, functional alignment This idea for functional aligment derives from asymmetry of siRNA in the assembly of the RNAi enzyme complex



1



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Document Gale Academic Onefile




Shrna And Sirna Of The Same Sequence Regulate The Same Subset Of Download Scientific Diagram




Gene Silencing By 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Modified Sirna A Prodrug Type Sirna Responsive To Reducing Environment Sciencedirect



Sidirect 2 0 Updated Software For Designing Functional Sirna With Reduced Seed Dependent Off Target Effect Bmc Bioinformatics Full Text




Sirna And Rnai Optimization Alagia 16 Wires Rna Wiley Online Library
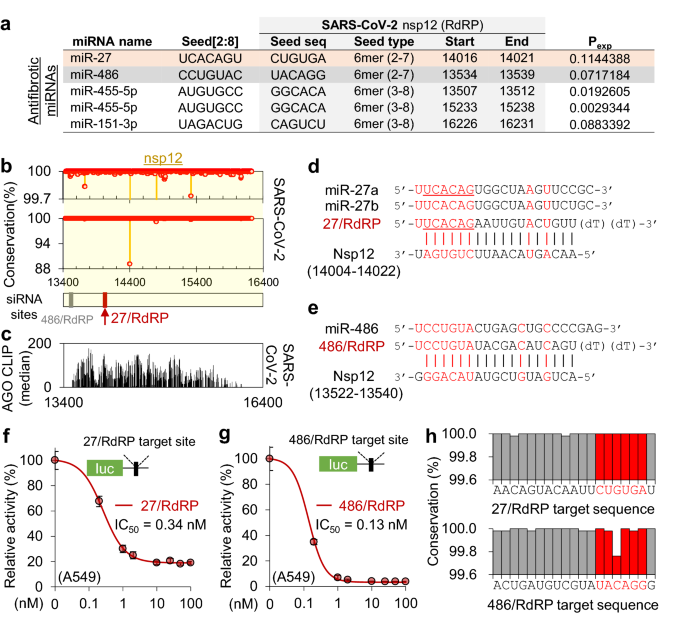



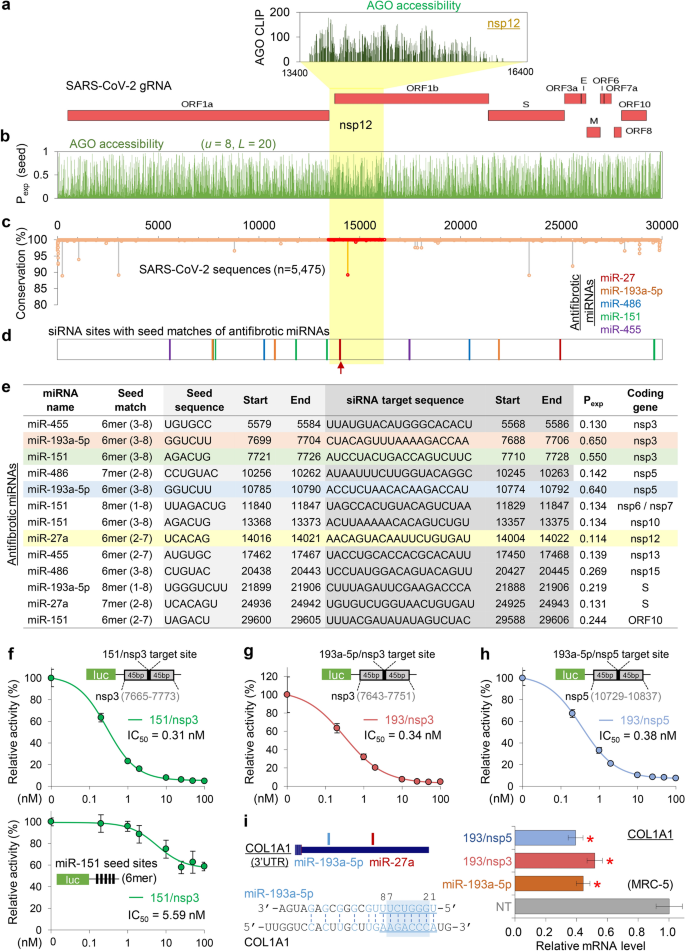
Ago Clip Based Imputation Of Potent Sirna Sequences Targeting Sars Cov 2 With Antifibrotic Mirna Like Activity Scientific Reports




Clinical Development Of Synthetic Sirna Therapeutics Sciencedirect




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
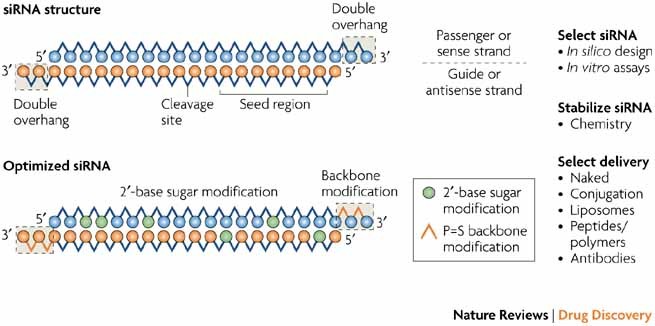



Interfering With Disease A Progress Report On Sirna Based Therapeutics Nature Reviews Drug Discovery




Pdf New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens Semantic Scholar




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Abstract Europe Pmc



1
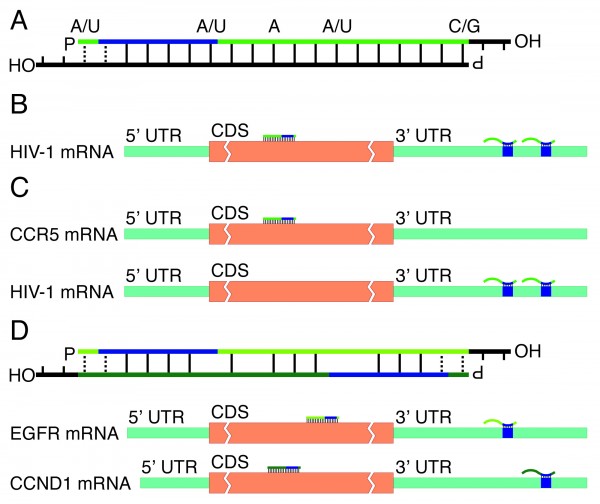



Unconventional Rna Interference Recent Approaches To Robust Rnai European Pharmaceutical Review




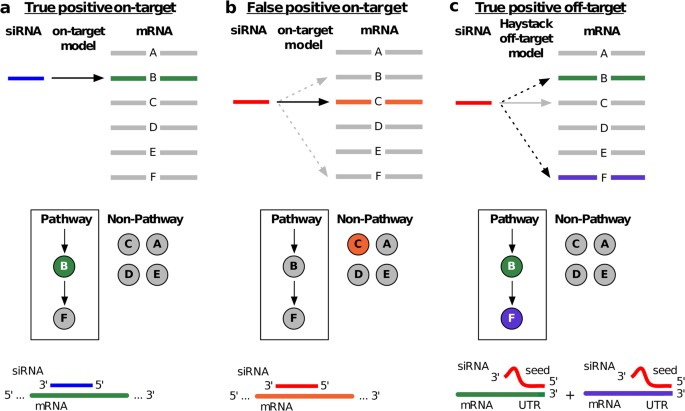
Seed Based Off Target Effects In Pooled Sirna Screens A An On Target Download Scientific Diagram




Seed Dependant Off Target Effect The Capability Of Sirnas To Induce Download Scientific Diagram



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link



Frontiers Synthetic Rnas For Gene Regulation Design Principles And Computational Tools Bioengineering And Biotechnology




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Pdf The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects Semantic Scholar
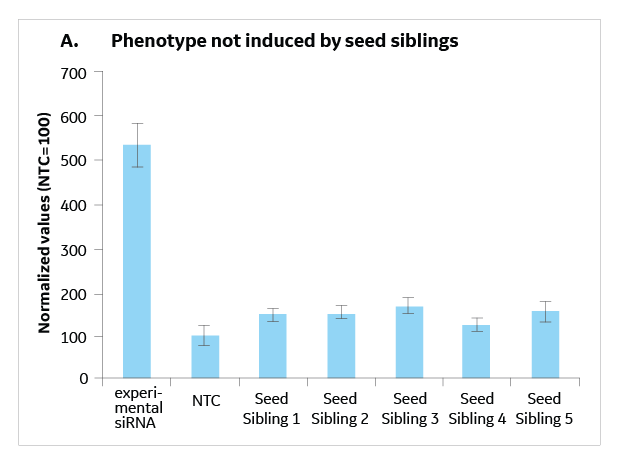



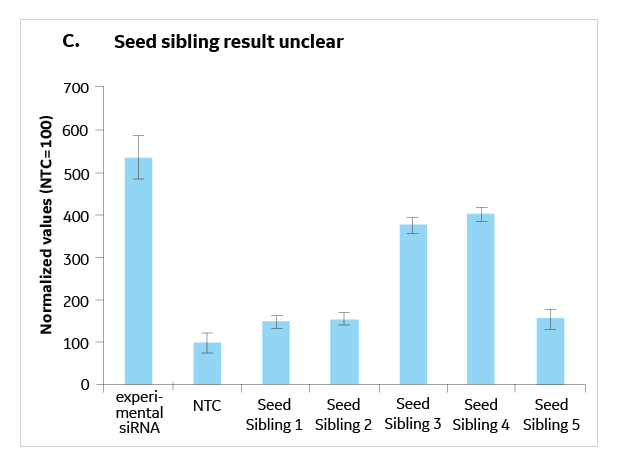
Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation
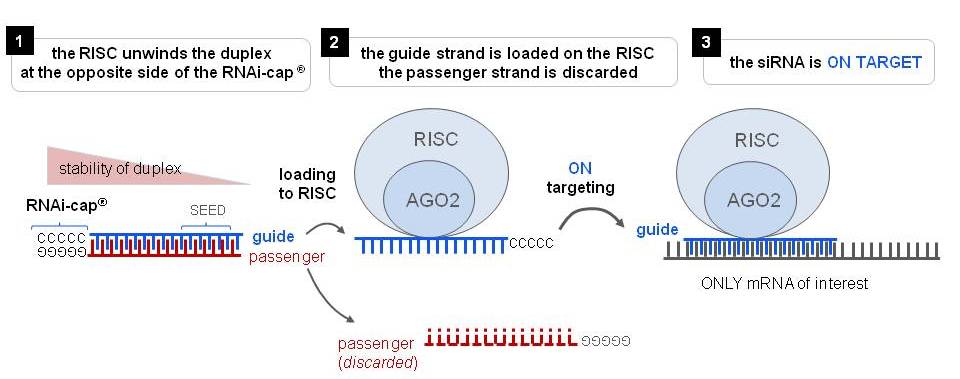



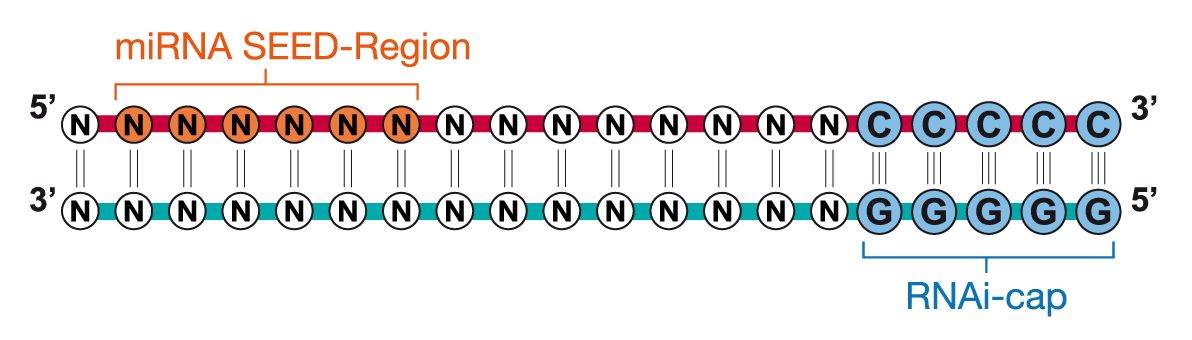
Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




Figure 3 Specific Silencing Of L392v Psen1 Mutant Allele By Rna Interference




Modification Of The Sirna Passenger Strand By 5 Nitroindole Dramatically Reduces Its Off Target Effects Zhang 12 Chembiochem Wiley Online Library



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
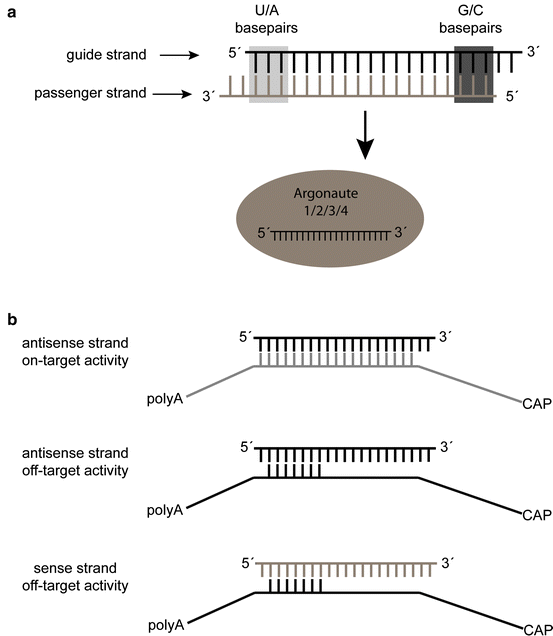



Sirna Design Principles And Off Target Effects Springerlink




Pdf Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar




Small Interfering Rna Wikipedia




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database




Pdf Sirna Design Software For A Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar
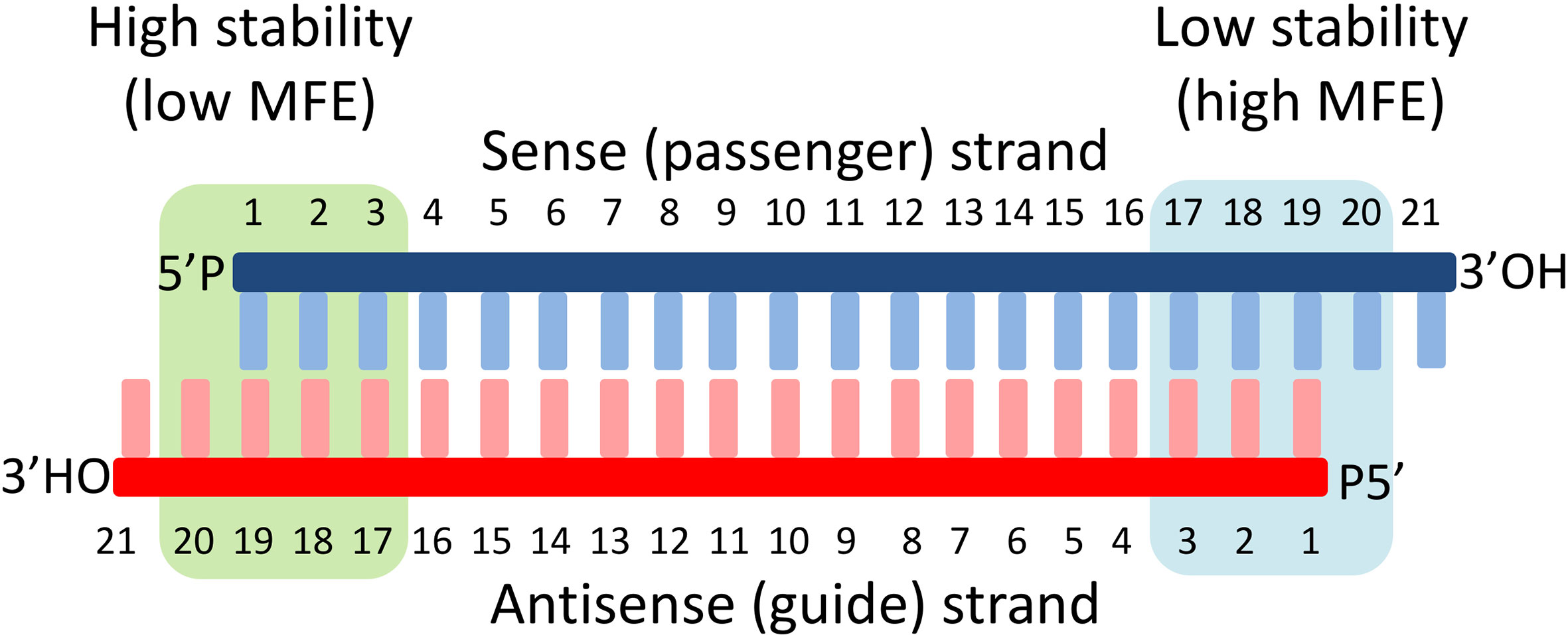



Frontiers Sirna Finder Si Fi Software For Rnai Target Design And Off Target Prediction Plant Science



Molecules Free Full Text Modulation Of The Rna Interference Activity Using Central Mismatched Sirnas And Acyclic Threoninol Nucleic Acids Atna Units Html




Figure S1 Schematic Representation Of Amirna Vs Sirna Approach A Download Scientific Diagram




Research Ui Tei Lab The University Of Tokyo
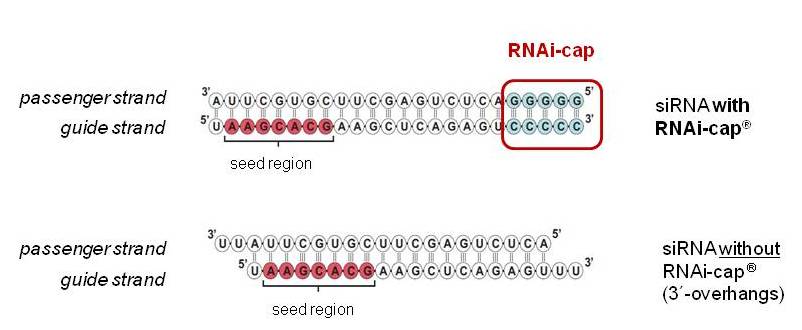



Riboxx Rna Technologies Better Silencing With Rnai Cap



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram



Sirna And Rnai Pricelist From Gene Link



Sirna Shrna Oligo Optimal Design




Pdf Sdrna Sirna With A Dna Seed For An Efficient And Target Gene Specific Rna Interference Semantic Scholar




Structures Of Sirna A And Dna Seed Containing Sirna B The Download Scientific Diagram




Seedseq Off Target Transcriptome Database



2




Graphical Representation Of Sirna Molecule A Sirna Duplex With Download Scientific Diagram
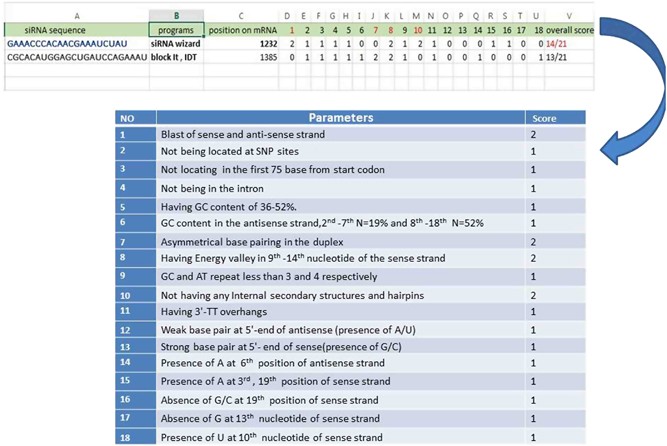



Precise And Efficient Sirna Design A Key Point In Competent Gene Silencing Cancer Gene Therapy




Reduced Seed Region Based Off Target Activity With Lentivirus Mediated Rnai
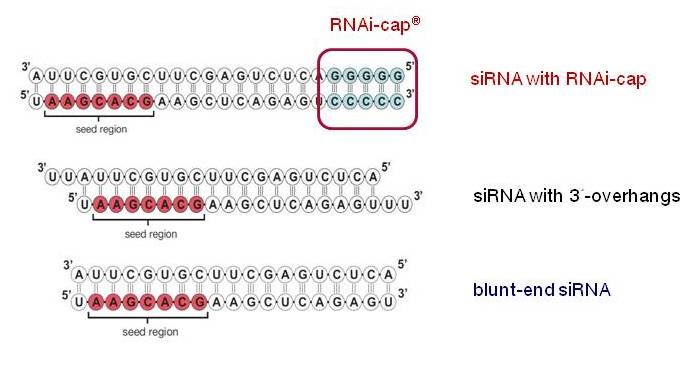



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Sirna




A Simple And Cost Effective Approach For In Vitro Production Of Sliced Sirnas As Potent Triggers For Rnai Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids
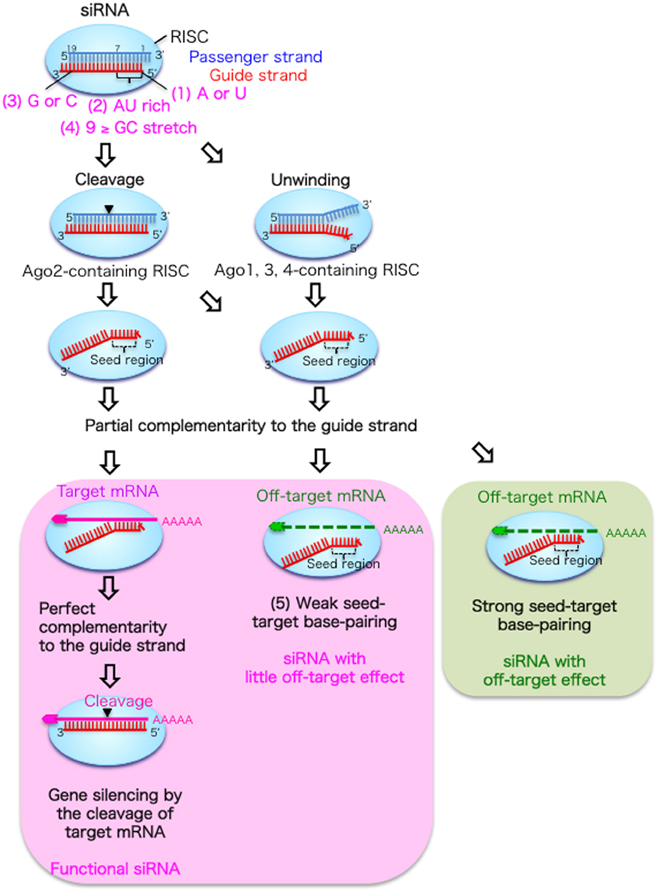



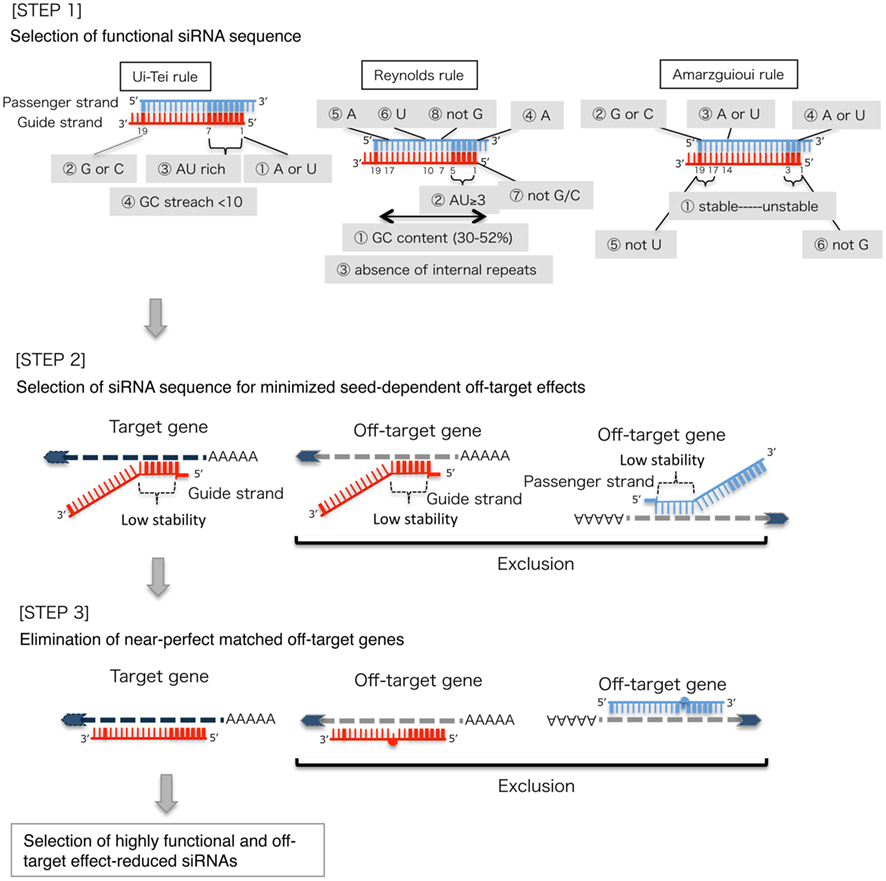
Frontiers Optimal Choice Of Functional And Off Target Effect Reduced Sirnas For Rnai Therapeutics Genetics



Sidirect



Frontiers Thermodynamic Control Of Small Rna Mediated Gene Silencing Genetics



2




An In Silico Analysis Of Effective Sirnas Against Covid 19 By Targeting The Leader Sequence Of Sars Cov 2 Pandey 21 Advances In Cell And Gene Therapy Wiley Online Library



Seed Sibling Controls For Rnai Hit Validation



Sirna Off Target Effects In Genome Wide Screens Identify Signaling Pathway Members Scientific Reports



2




Cell Free Reconstitution Reveals The Molecular Mechanisms For The Initiation Of Secondary Sirna Biogenesis In Plants Pnas



Gess




Rational Design Of Therapeutic Sirnas Minimizing Off Targeting Potential To Improve The Safety Of Rnai Therapy For Huntington S Disease Sciencedirect




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Sciencedirect



Ijms Free Full Text Is The Efficiency Of Rna Silencing Evolutionarily Regulated Html



Ago Clip Based Imputation Of Potent Sirna Sequences Targeting Sars Cov 2 With Antifibrotic Mirna Like Activity Scientific Reports



Plos One In Silico Design And Experimental Validation Of Sirnas Targeting Conserved Regions Of Multiple Hepatitis C Virus Genotypes



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects
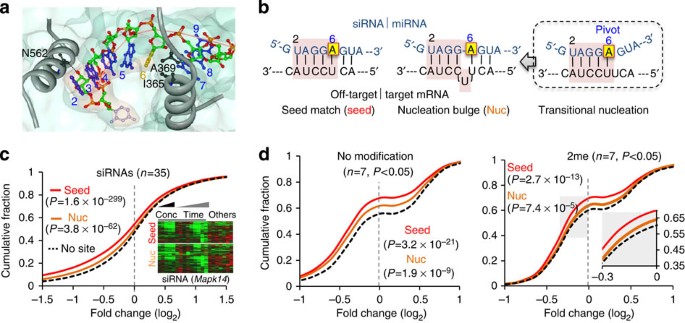



Abasic Pivot Substitution Harnesses Target Specificity Of Rna Interference Nature Communications




Selection Of Chemical Modifications In The Sirna Seed Region That Repress Off Target Effect Springerlink



2
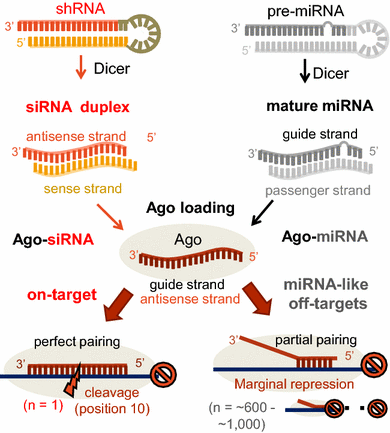



Evaluation And Control Of Mirna Like Off Target Repression For Rna Interference Springerlink



Plos Computational Biology The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Ayn Cell Culture




Effects Of Dna Substitutions In The Non Seed Duplex Subdomains A B C Download Scientific Diagram
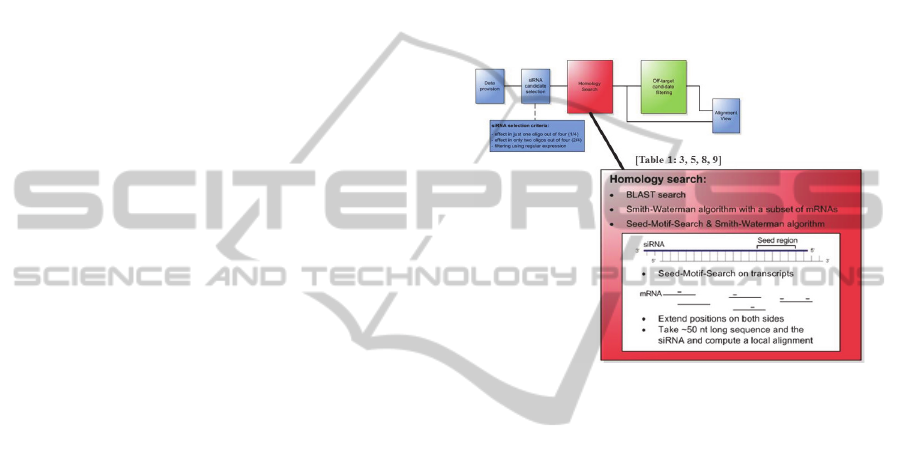



New Algorithm For Analysis Of Off Target Effects In Sirna Screens




2 O Methyl At Mer Guide Strand 3 Termini May Negatively Affect Target Silencing Activity Of Fully Chemically Modified Sirna Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Modified Sirna Structure With A Single Nucleotide Bulge Overcomes Conventional Sirna Mediated Off Target Silencing Molecular Therapy
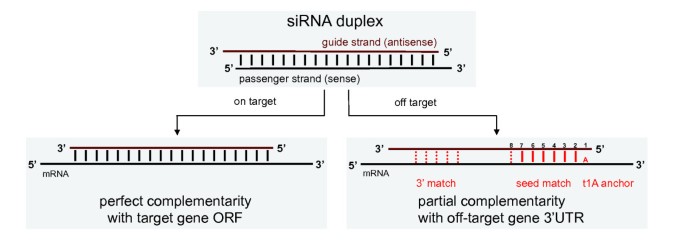



Off Target Effects Dominate A Large Scale Rnai Screen For Modulators Of The Tgf B Pathway And Reveal Microrna Regulation Of Tgfbr2 Silence Full Text
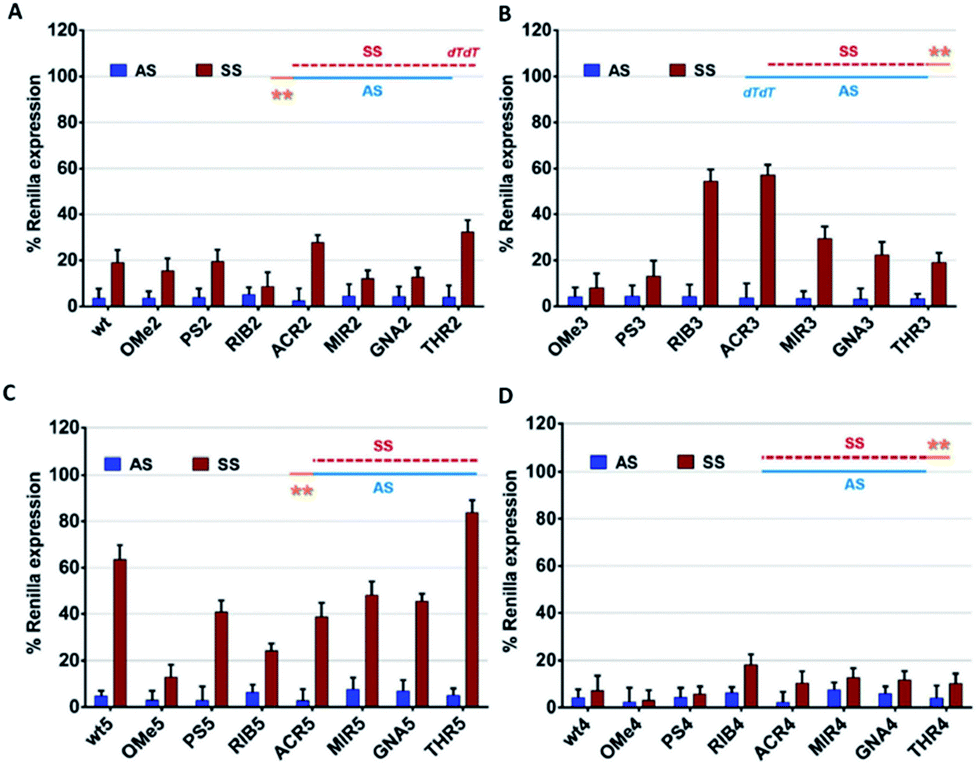



Exploring Paz 3 Overhang Interaction To Improve Sirna Specificity A Combined Experimental And Modeling Study Chemical Science Rsc Publishing




Tolerance For Mismatches Between An Sirna And Its Target Sirna Seed Download Scientific Diagram




Rational Design Of Highly Efficient Artificial Mirna Mirna Download Scientific Diagram




Effects Of 2 Bp Long Dna Substitutions In The Non Seed Region Of Sirna Download Scientific Diagram



2




Effective Gene Silencing Activity Of Prodrug Type 2 O Methyldithiomethyl Sirna Compared With Non Prodrug Type 2 O Methyl Sirna Sciencedirect




Ago Accessible Anticancer Sirnas Designed With Synergistic Mirna Like Activity Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿