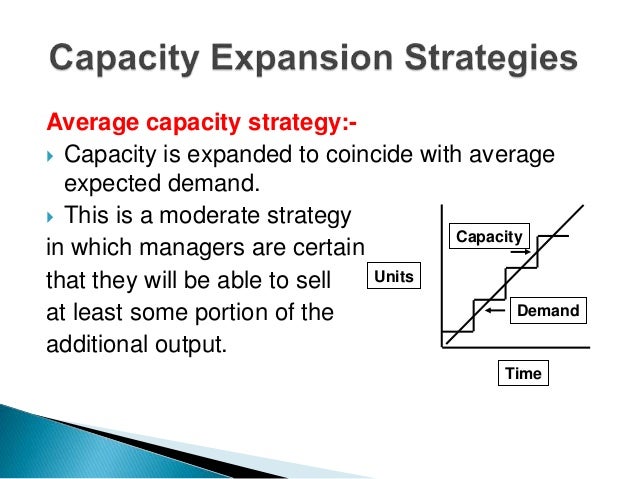
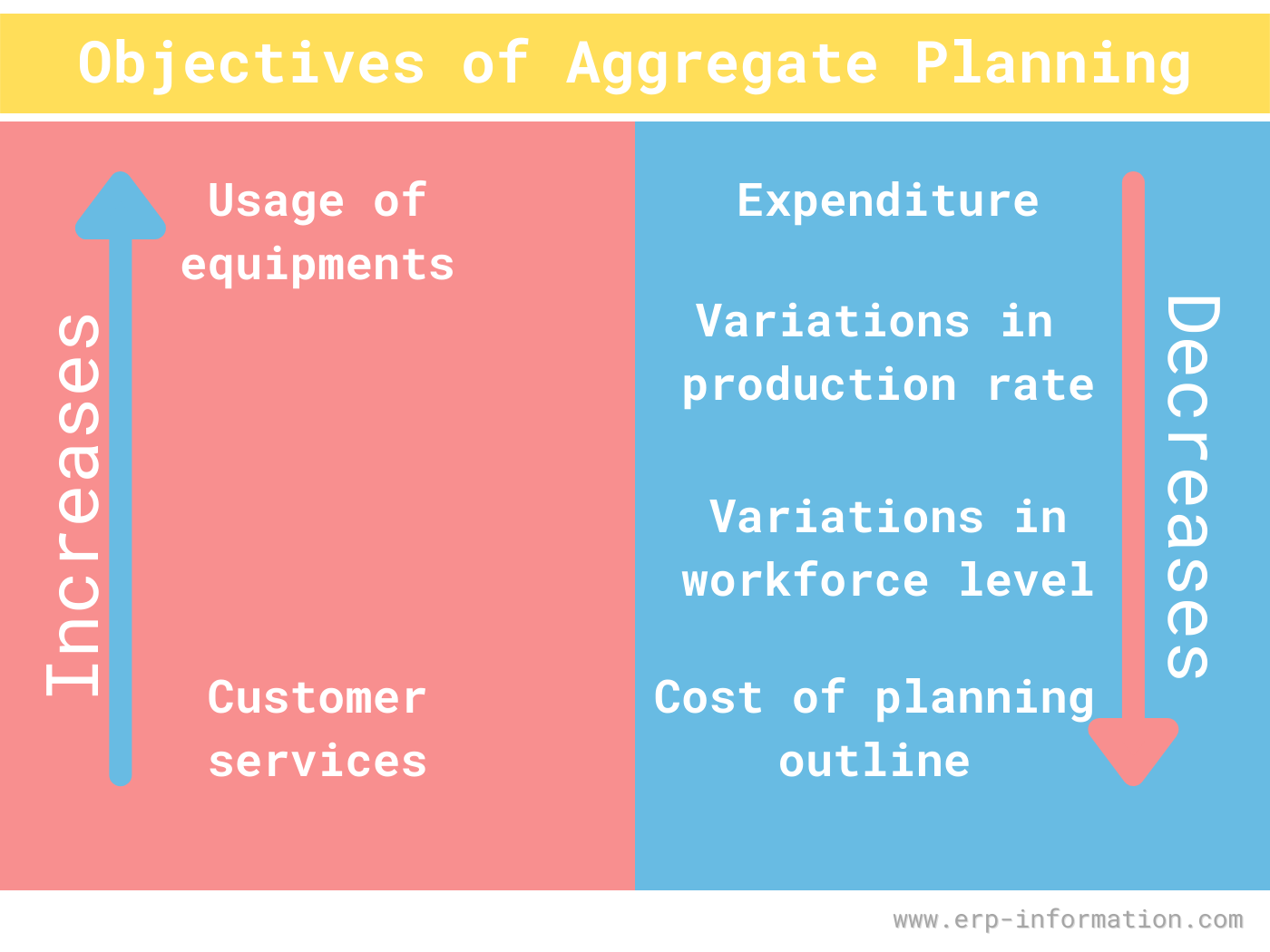
Strategies to Meet Uneven Demand Example Level capacity strategy Chase demand strategy 1) Level capacity strategy The organization manufactures or produces at a constant rate of output ignoring any changes or (rise/fall) in customer demand levels Advantages Utilization of operational resources at all times Efficient production levels can be held at a constant rateIf Casey's company follows an average strategy for capacity, it'll align its capacity with the average expected level of demand forecasted For example, Casey's number crunchers may have Capacity, Route Planning, and Scheduling An Efficient Trifecta Once you've got your highlevel (capacity) plan in place, you can use it as a guide for scheduling and route planning You'll want to use all three together to achieve the highest level of logistical efficiency We are here to help with all three
Cascading Scorecards Calculated Roll Up Intrafocus
Level capacity strategy example
Level capacity strategy example-CAPACITY BUILDING STRATEGY The purpose is to achieve a high level of ownership and motivation on the part of GRZ 2 Capacity Assessment/Identification of Gaps/Needs At the beginning of the program, the team conducted capacity assessments to ascertain (For example, the initial capacity building plan targeted nationallevel GRZ staff23 Strategic Objective 3 – Technical Capacity 9 24 Strategic Objective 4 – Coordination and Programme Management 12 25 Strategic Objective 5 – Institutionalisation of CD 14 30 Strategy Implementation 15 40 Financing the CD Strategy 18 50 Monitoring the CD Strategy 19



Capacity Utilization Definition Example And Economic Significance
The three levels of strategy are Corporate level strategy This level answers the foundational question of what you want to achieve Is it growth, stability, or retrenchment? Level Production Strategy We are going to find the requirements for the entire period of the plan and also produce the average amount that is needed per month in order to meet the plan First we are going to determine the total average requirements per month Avg requirements = total number of requirements – opening inv closing invThe idea here is that a level schedule is used during consistent periods and the chase strategy is used during months with fluctuating demand This can be helpful in seasonal business For example, a company that made Halloween chocolates, may maintain a level schedule for 9 months of the year and then use a chase strategy during the weeks
Capacity is often measured in hours available to be worked by employees And in this context, "planning" is the act of scheduling employee hours against a fixed or expected amount of work Example A company has 10 employees Each employee works 40 Capacity planning strategy involves the process used to determine the resources manufacturers need to meet the demand for their products or services The level of capacity directly relates to the amount of output in the form of goods and services manufacturers can produce to satisfy customer demand Capacity planning strategies can guide Capacity Planning It's pprove/cancel projects
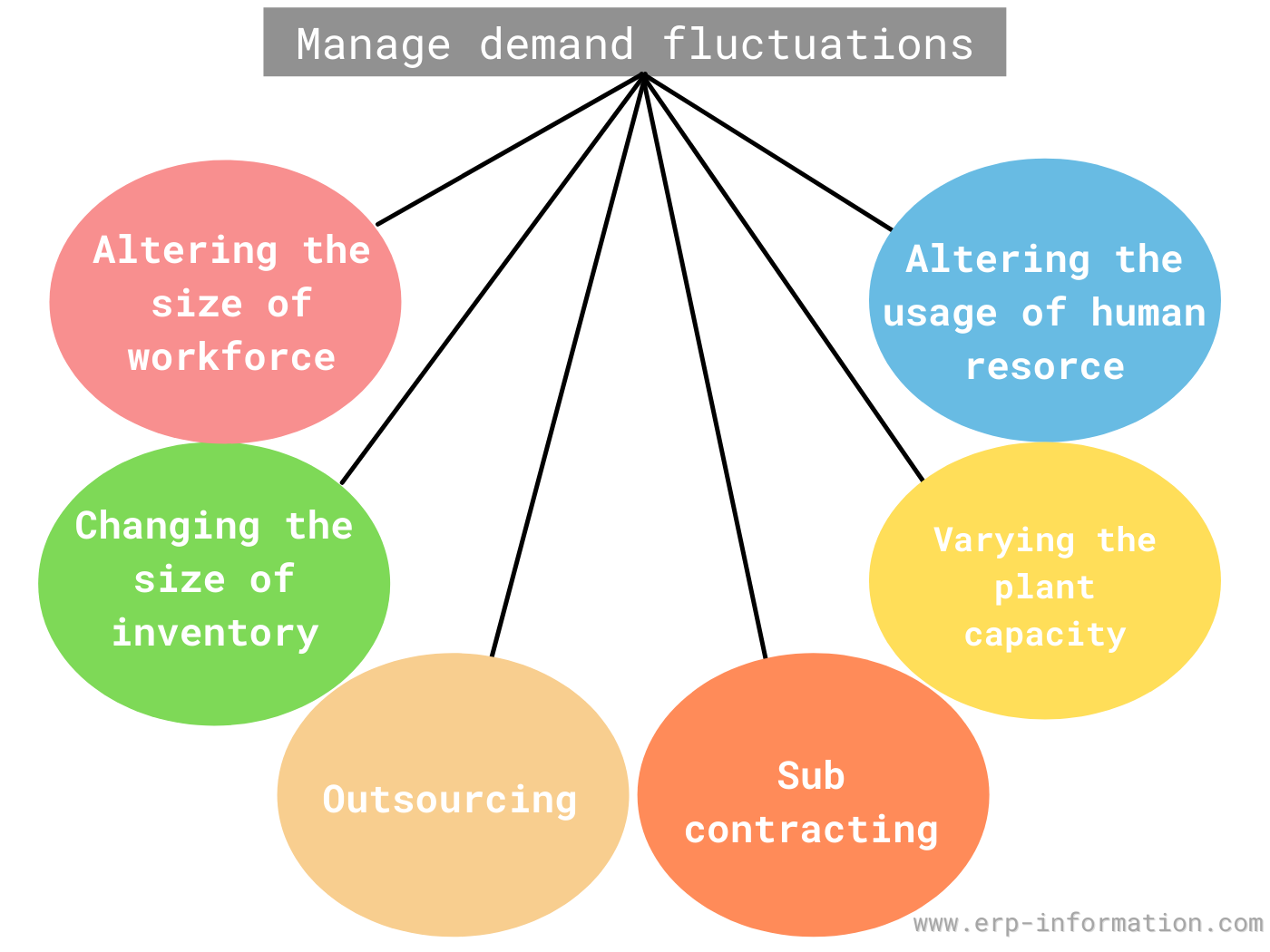
The IT strategy roadmap example section should describe the technology directions that will best support the business and a highlevel plan for getting there from the current state Because it can be difficult to foresee what new technology developments would benefit a given business, it's sometimes easy to go in a direction that ends upUse break even analysis to evaluate capacity alternatives This module examines how important strategic capacity planning is for products and services The overall objective of strategic capacity planning is to reach an optimal level where production capabilities meet demand Capacity needs include equipment, space, and employee skillsThe level capacity strategy, the focus is on the process where product output remains at a somewhat fixed level and increases/decreases in demand are satisfied through strategic decisions of utilizing inventory (maintain buffer stock), outsourcing and backorders In comparison to level capacity strategy is adjusting capacity to follow




What Is S Op Sales And Operations Planning Explained Anaplan



Capacity Management
The advantages of the level capacity strategy include 1 The utilization of operational resources throughout the year 2 Efficient level of production can be maintained 3 Decreases the marginal cost The disadvantages of the level capacity strategy include 1 If there is any change in the demand of the customer there is a risk ofThe Extremes Level Strategy Chase Strategy Production equals demand Production rate is constant Basic Aggregate Planning Strategies for Meeting Demand Level capacity strategy Keeping work force constant and maintaining a steady rate of regulartime output while meeting variations in demand by a combination of options (such as using inventoriesExplain about the level capacity strategy Level capacity strategy The organisation produces or manufactures at a constant rate of output avoiding any changes or fluctuations within customer demand levels This frequently implies stockpiling or higher holdings of inventory while customer demand levels reduce




Coronavirus S Impact On Supply Chain Mckinsey



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System
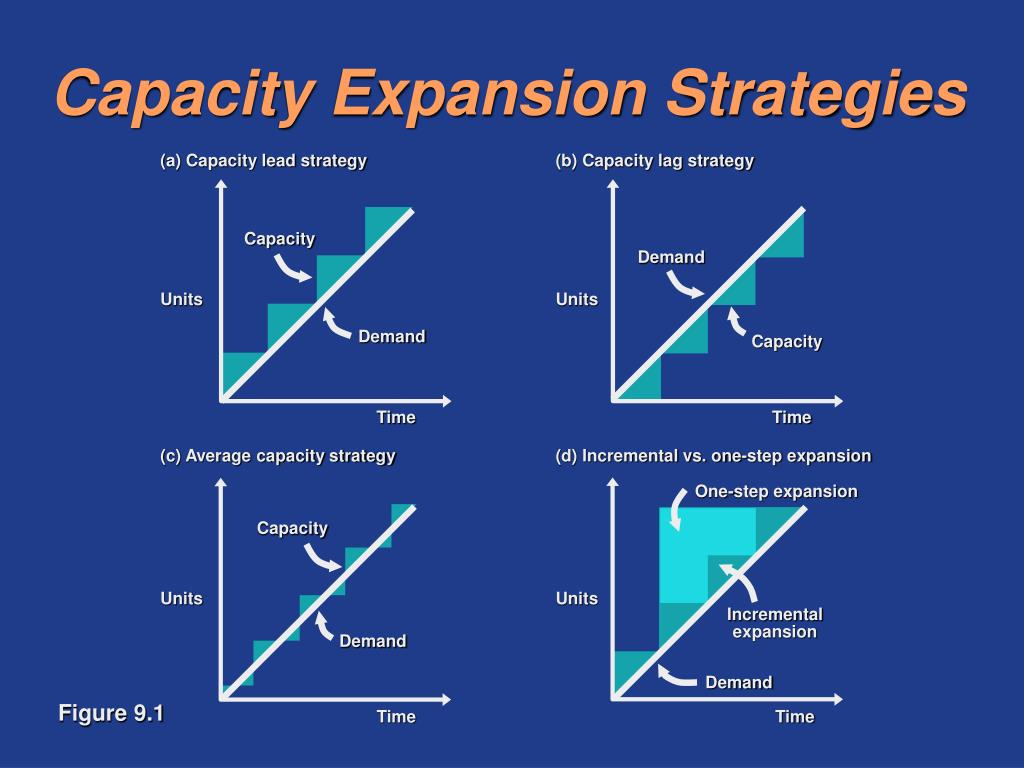
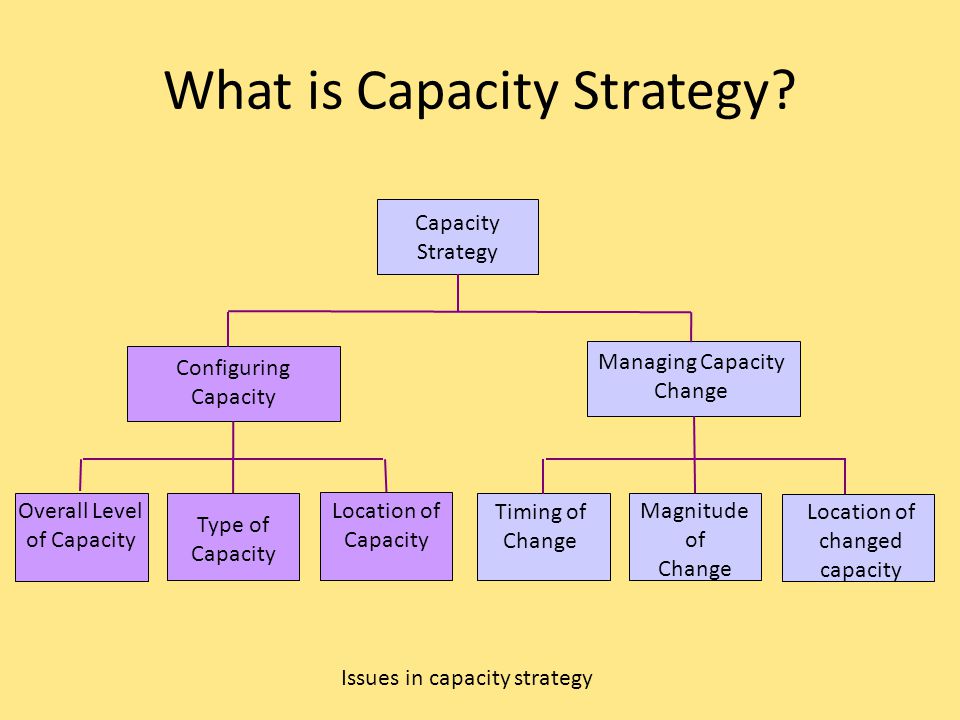
Lead Strategy An upfront investment in more capacity that you need This can be done when capacity is inexpensive or difficult to obtain For example, a new vineyard anticipates using less than 10 acres of land in its first 5 years but purchases 100 acres of land as a long term investment in the business One of the strategic choices that a firm must make as part of its manufacturing strategy There are three commonly recognized capacity strategies lead, lag, and tracking A lead capacity strategy adds capacity in anticipation of increasing demand A lag strategy does not add capacity until the firm is operating at or beyond full capacityBusiness unit level strategy This level focuses on how you're going to compete




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Slides For Chapter 10 Strategic Capacity Honda On July 18 Announced Two New Plants In Argentina Honda Will Spend 100 Million On A New Compact Car Ppt Download
Capacity expansion is a credible deterrent strategy if capacity costs are very high Otherwise, if the cost of adding capacity is low or capacity can be utilized for other purposes, it would be relatively easy for rivals to enter For example, DuPont used capacity expansion to increase its market share in the titanium dioxide market For example, a software service that offers an SLA to customers plans the capacity required to meet service levels based on sales forecasts Component Capacity Management Low level capacity management such as planning the software licenses and disk space required for a single applicationA firm should tend toward a levelcapacity strategy, particularly in its personnel policies, when employees are required to have high skill levels and to work with minimal supervision and must exercise personal discretion in dealing with customers Such jobs typically have high recruitment and training costs, so low turnover is essential These



What Is Aggregate Planning 3 Strategies For Aggregate Production Planning




Cascading Scorecards Calculated Roll Up Intrafocus
Capacity Planning Capacity planning is a longterm strategic decision that establishes a firm's overall level of resources It extends over a time horizon long enough to obtain those resourcesusually a year or more for building new facilities or acquiring newCombination Strategy (cont) –Produces at or close to full capacity for some part of the cycle –Produces at a lower rate (or does not produce) during the rest of the cycle –Makes use of available capacity, yet limits inventory buildup and inventory carrying costs On the other hand, the operations of McDonald's restaurants are dependent on the management's ability to build capacity The company's strategy aims to eliminate capacity constraints through the utilization of qualitative and quantitative forecasting methods References Makridakis, S, (08) Forecasting methods and applications New




Capacity Planning Everything You Need To Know Clicktime




Example Of Indicators On The Immediate Surroundings Download Scientific Diagram
Under the chase strategy, production is varied as demand varies With the level strategy, production remains at a constant level in spite of demand variations In companies that produce to stock, this means that finished goods inventory levels will grow during low demand periods and decrease during high demand periodsChase Capacity Management Opposite to the level capacity management is the chase capacity, " organisations could decide to match capacity and demand by altering the availability of resources This might be achieved by employing more people when it is busy and adopting strategies such as overtime and additional shiftsThis revision video provides an overview of the concept of capacity, capacity utilisation and some of the issues facing businesses operating at low or high u




Everything About Capacity Planning Strategies Its Benefits




Strategic Capacity Planning Capacity Utilization
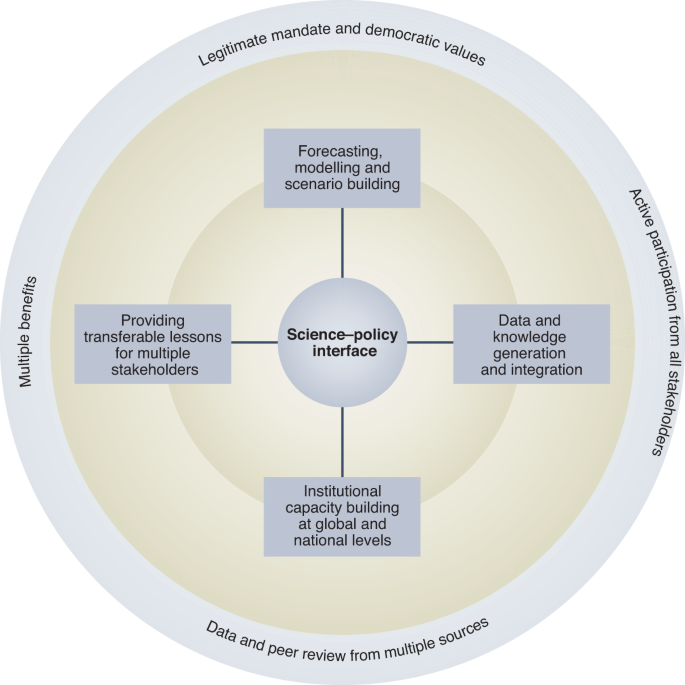
Corporate strategy, on the other hand, is the top management plan concerning the whole organization It's the master plan that directs the company towards success The more appropriate corporatelevel strategy is, the more it would increase the chances for the success of your organizationIn order to use the level capacity strategy, variations in demand are met by A varying output during regular time without changing employment levels B varying output during regular time by changing employment levels C varying output by changing overtime levels D using combination of inventories, overtime, part time, and back orders Organization and systemslevel measurement strategies such as those used to operationalize Lang's system capacity and readiness offer an example Working toward a more complete body of evidence showcasing outcomes on multiple levels would support more informed decision making around capacitybuilding interventions and how best to deliver them




Roadmap Scaled Agile Framework




What Is Resource Leveling Techniques And Examples Asana
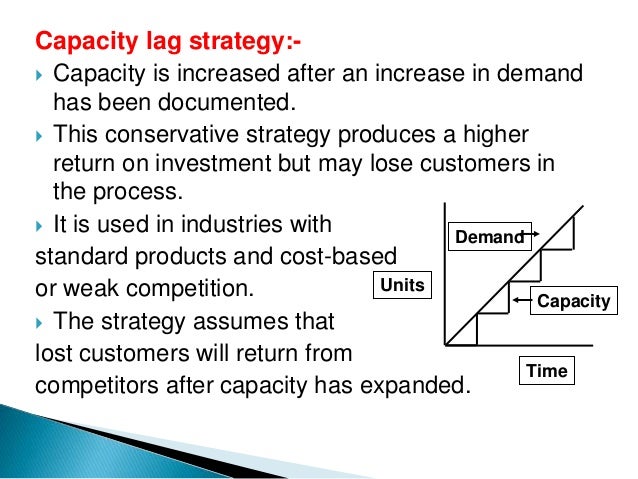
Functional level strategies will be specific and will apply to a variety of functional areas (departments) For example, building on the diversification example, the functional level strategies that support that business level strategy might be R&D Redesign product Marketing Implement new advertising planBelow are some of the most popular capacity management strategies #1 – Lag Strategy Using this conservative approach, a manager determines the capacity and then waits until there is an actual steady increase in demand Then, the manager raises the production capabilities to a level to satiate the current market need An approach to aggregate planning that attempts to match supply and output with fluctuating demand Depending on the product or service involved, the approach can incur costs by the ineffective use of capacity at periods of low demand, by the need to recruit or lay off staff, by learningcurve effects, and by a possible loss of quality The advantages include low storage




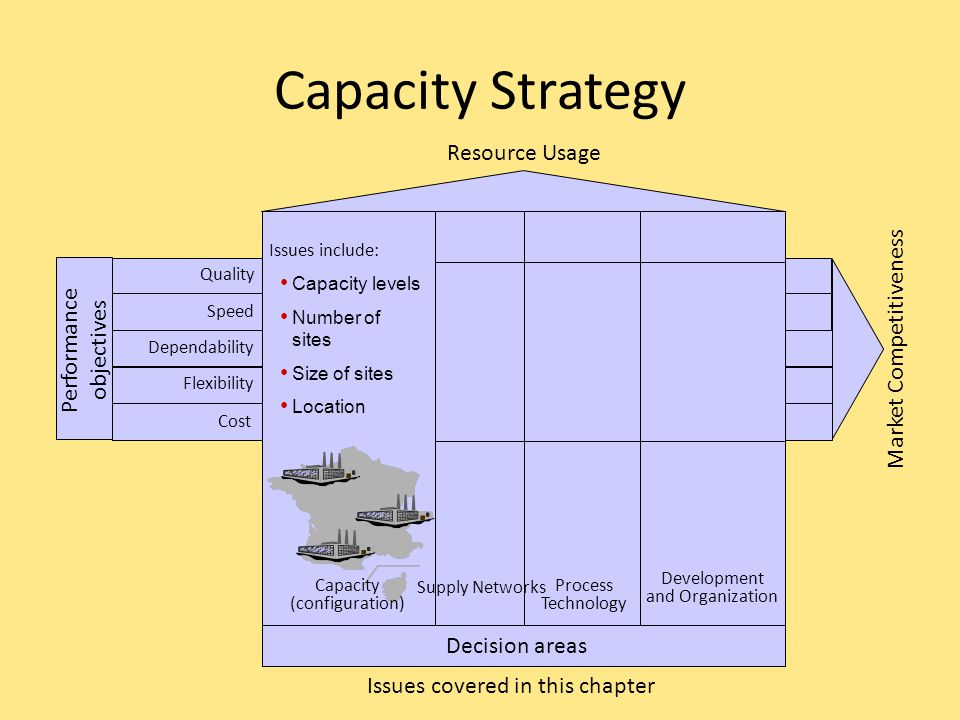
4 Capacity Strategy



Capacity Planning For Project Managers How To Plan Your Team S Time
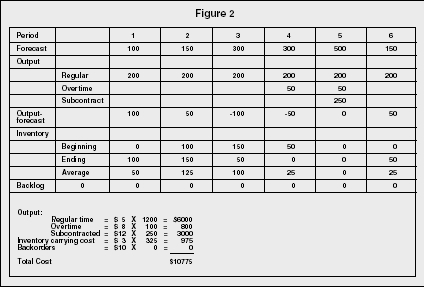
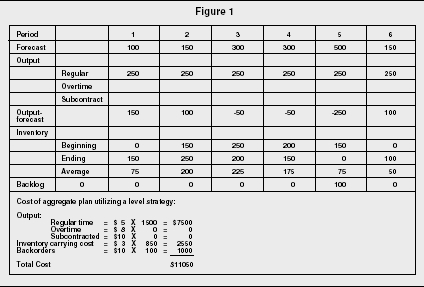
Practical examples of models in capacity planning for different production modes include 1 Make to Stock (MTS) Make to Stock is common within discreet manufacturing and process manufacturing As these operations often have complex multilevel BOMs, capacity planning must include planning for subprocesses required to produce components Strategic capacity planning is how companies figure out the production capacity needed in order to meet consumer demand It's a highly difficult process because of several reasons The first reason is because it relies on accurate demand forecasting Most businesses do not do demand forecasting very well, often due to a lack of understandingInputs Period 1 2 3 4 5 6 Forecasted demand (Number of parttime workers 6 12 18 15 13 14 Example 1 Level strategy Each period is hours • From the beginning



Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download




Pdf Capacity Investment Under Responsive Pricing Implications Of Market Entry Choice
A level strategy seeks to produce an aggregate plan that maintains a steady production rate and/or a steady employment level In the context of the problem posted by you following the level strategy means incurring additional subcontracting costs at least twice This is to offset the shortfall in production because of the level strategy 3 Hybrid strategy for an aggregate planning As the name indicates, the Hybrid strategy is an integration of both level and chase strategies to get a better result It maintains a sufficient balance between stock level, recruiting, termination and production rate In the hybrid strategy of aggregate planning, the organizations build upCapacity Decisions are Strategic 1 Capacity decisions have a real impact on the ability of the organizationto meet future demands for products and services 2 Capacity decisions affect operating costs 3 Capacity is usually a major determinant of initial cost Typically, the greater the capacity of a productive unit, the greater its cost 4




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Solved Question 4 A Compare And Contrast The Level And Chegg Com




Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download




Everything About Capacity Planning Strategies Its Benefits



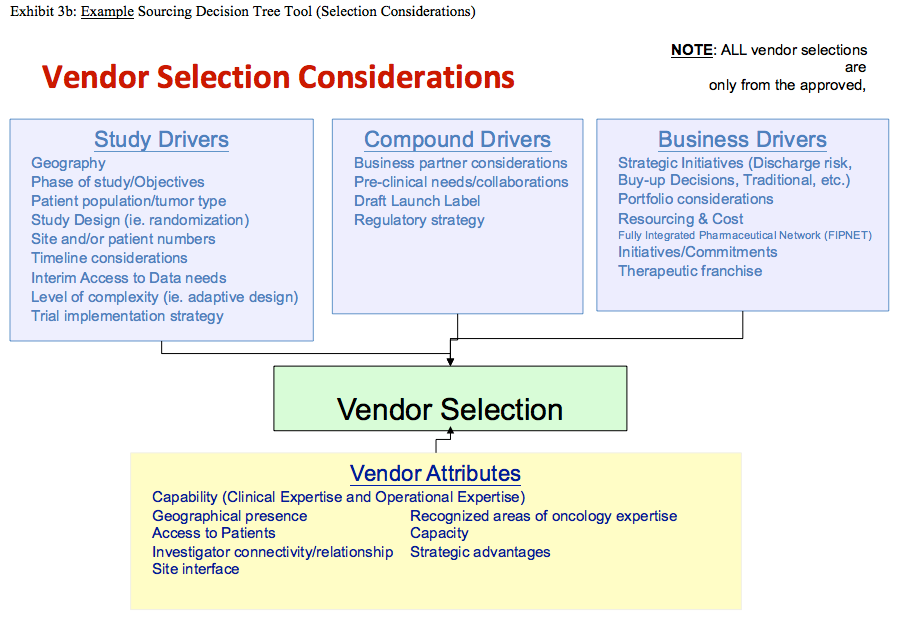
Developing A Logical Sourcing Strategy




Pi Objectives Scaled Agile Framework




Capacity Utilization Manufacturing Kpi Examples Sisense




Capacity Planning Meaning Classification And Its Goals



Kcajglqb75vpom




Capacity Utilization Definition Example And Economic Significance
.PNG)



Process Landscape Aris Bpm Community




Network Based Social Capital And Capacity Building Programs An Example From Ethiopia Topic Of Research Paper In Sociology Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub




Aggregate Planning Definition Importance Strategies Management And Advantages



Capacity Planning For Project Managers How To Plan Your Team S Time




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute



2



Concept Of Capacity Planning And It S Procedure Importance Management Study Hq




Solved 17 Which Of The Following Is Not An Example Of Chegg Com




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps




Mmi Strategy 6



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq



Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute




Capacity Building Wikipedia




Do Not Copy Chapter 10 Capacity Management In Service Operations Ppt Download



Capacity Management




Basic Strategies Level Capacity Strategy Chase Demand Strategy Ppt Download



Aggregate Planning



Capacity Management Definition Strategies Example



Ppt Capacity And Aggregate Planning Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Aggregate Planning Strategy Organization Levels System Examples Model Type Company System



Roadmap Scaled Agile Framework
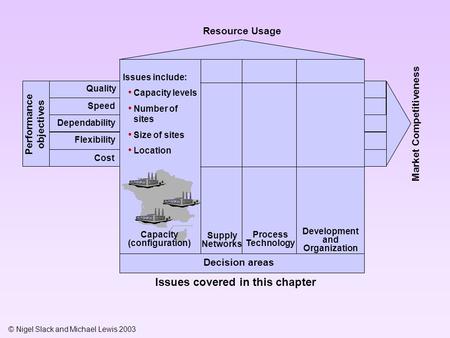



Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute



7 Practical Ways To Prioritize Your Product Backlog
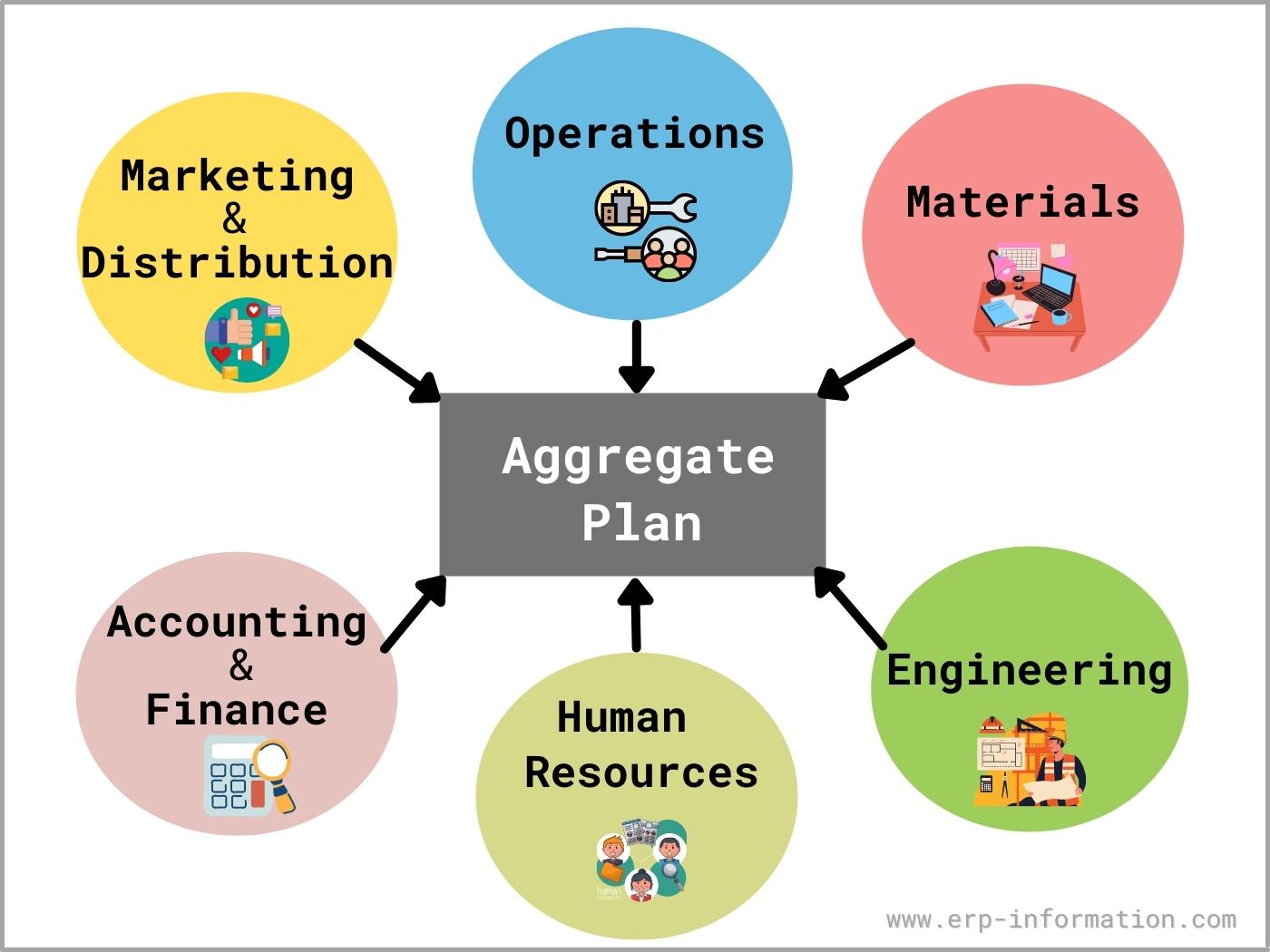



What Is Aggregate Planning 3 Strategies For Aggregate Production Planning



Workshop In Nouvelle Aquitaine Fr Eo4geo




Ops Mngt Lesson 6 Exercise 25 10 07 Sergio S Blog
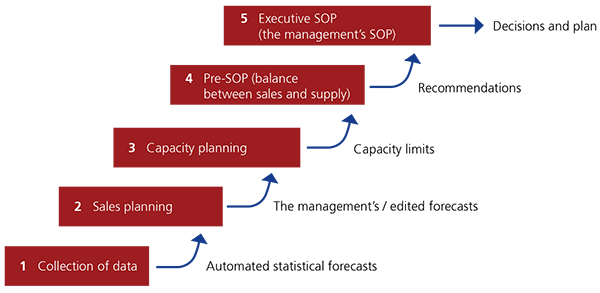



Sales And Operations Planning Relex Solutions
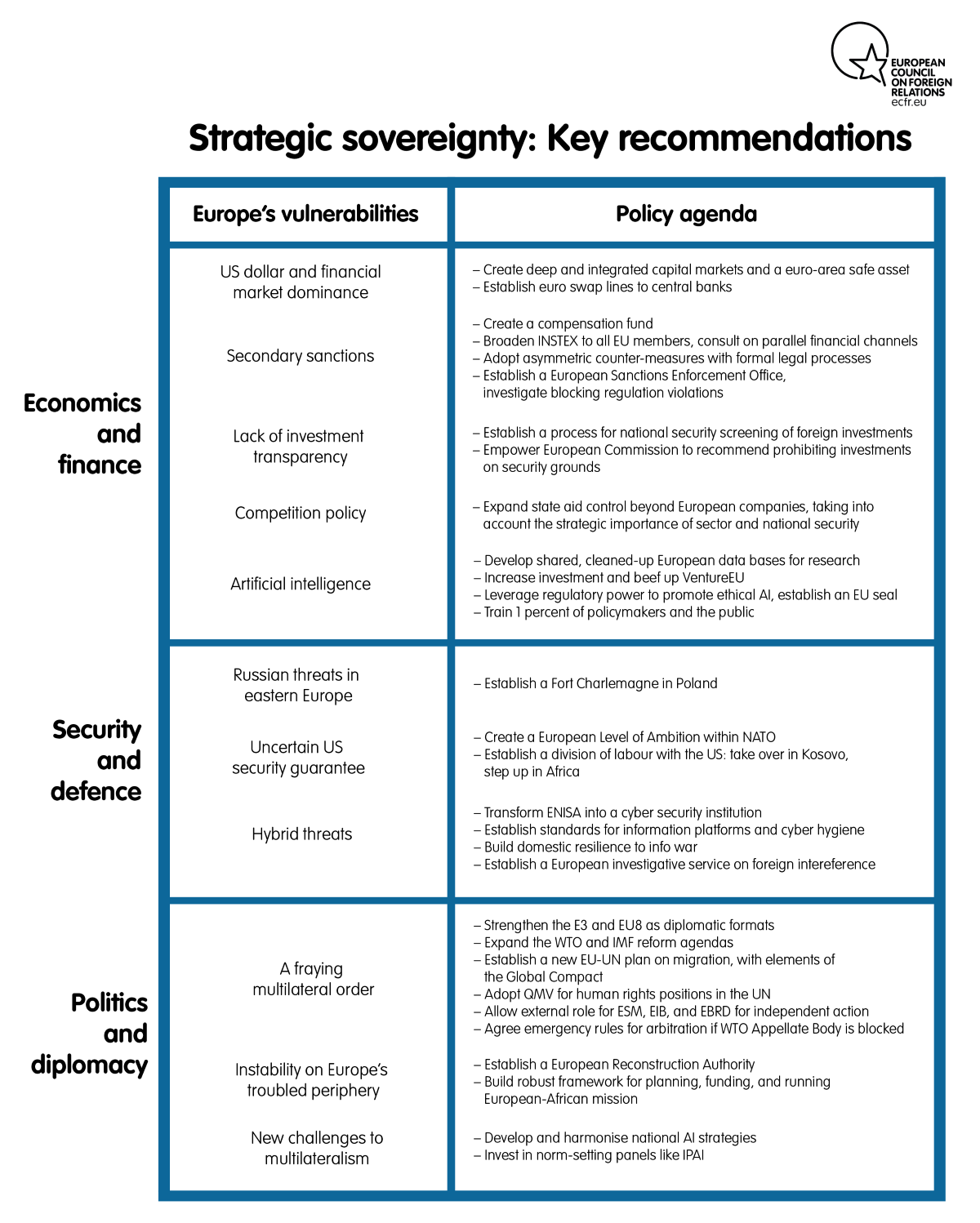



Strategic Sovereignty How Europe Can Regain The Capacity To Act European Council On Foreign Relations




Features And Capabilities Scaled Agile Framework




Long Rang Capacity Planning Ppt Download
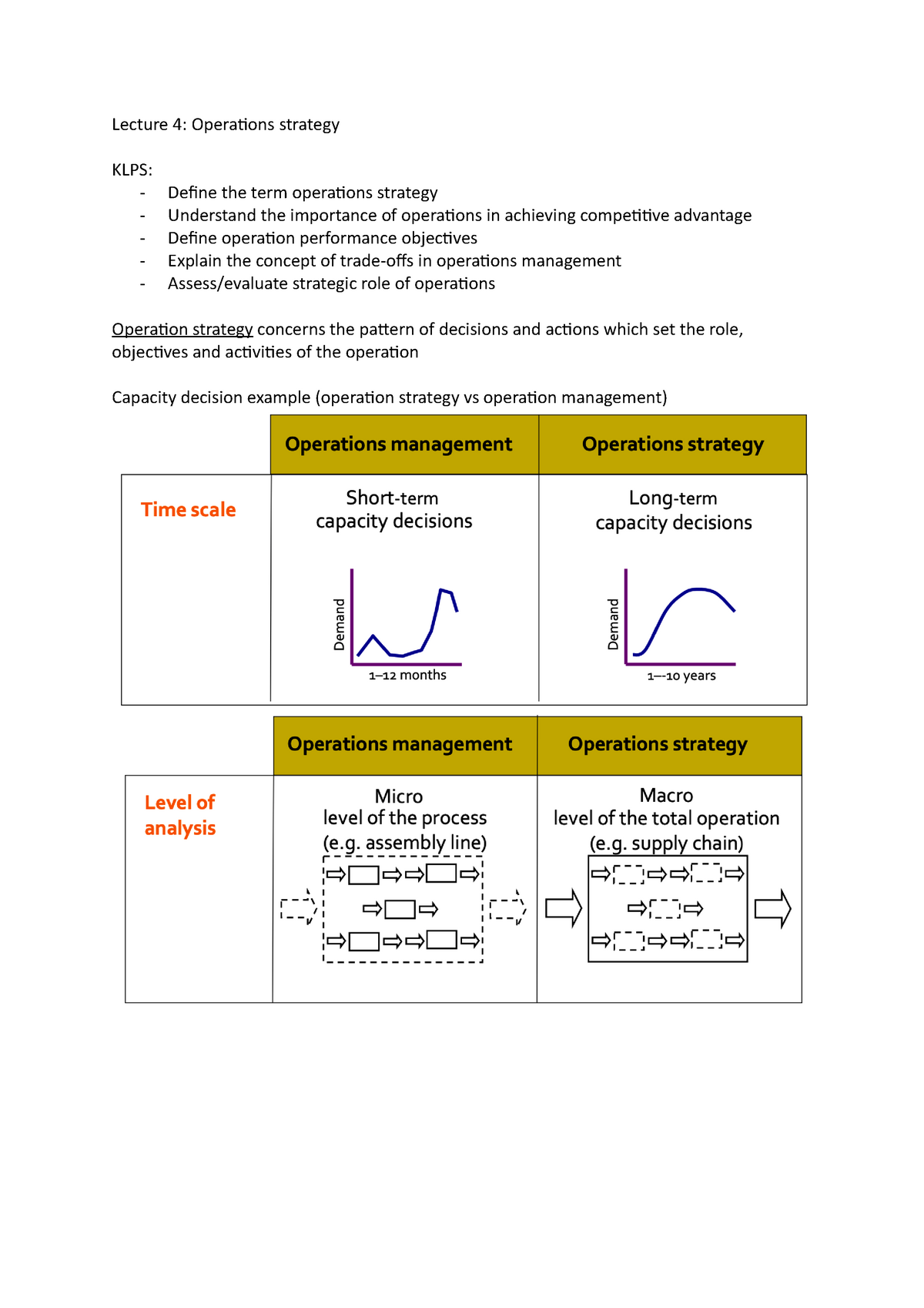



Lecture 4 Operations Strategy Lecture 4 Operations Strategy Klps Define The Term Operations Studocu




Amazon Business Strategy Insights Of Its Core Operations And Investment
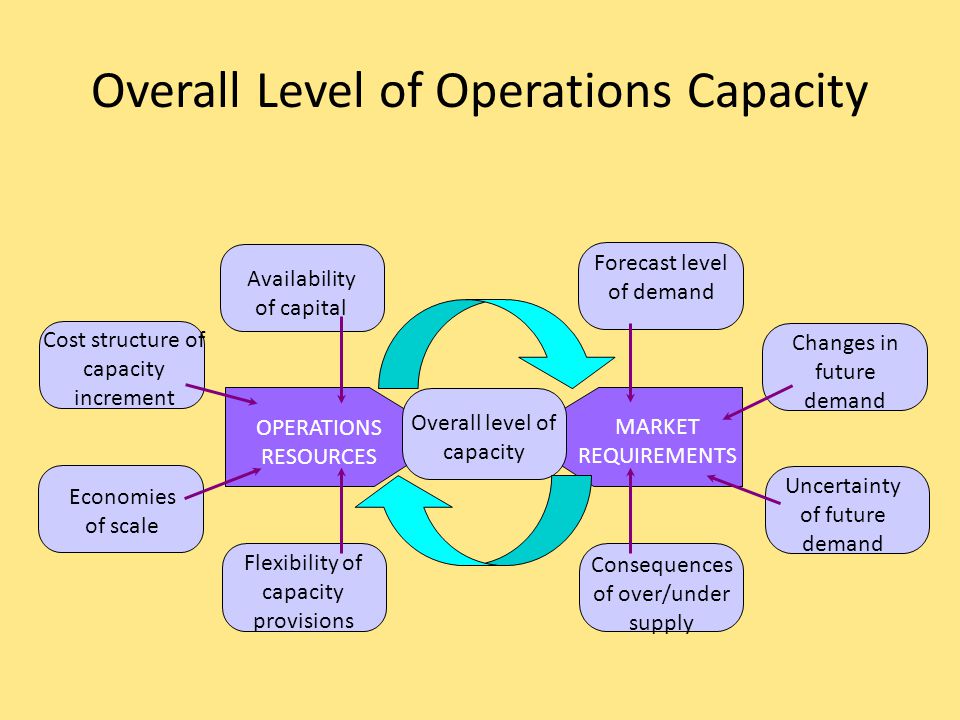



Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download




Tor Wateraid




Roadmap Scaled Agile Framework




Capacity Strategy Some Factors Influencing The Overall Level Of Capacity Forecast Level Of Demand Consequences Of Over Under Supply Availability Of Ppt Download




Capacity Planning Everything You Need To Know Clicktime



3




3 Types Of Capacity Planning Strategies Valq




Capacity Planning 3 Methods How To Implement Them Optimoroute




Capacity Planning And Control Ppt Download
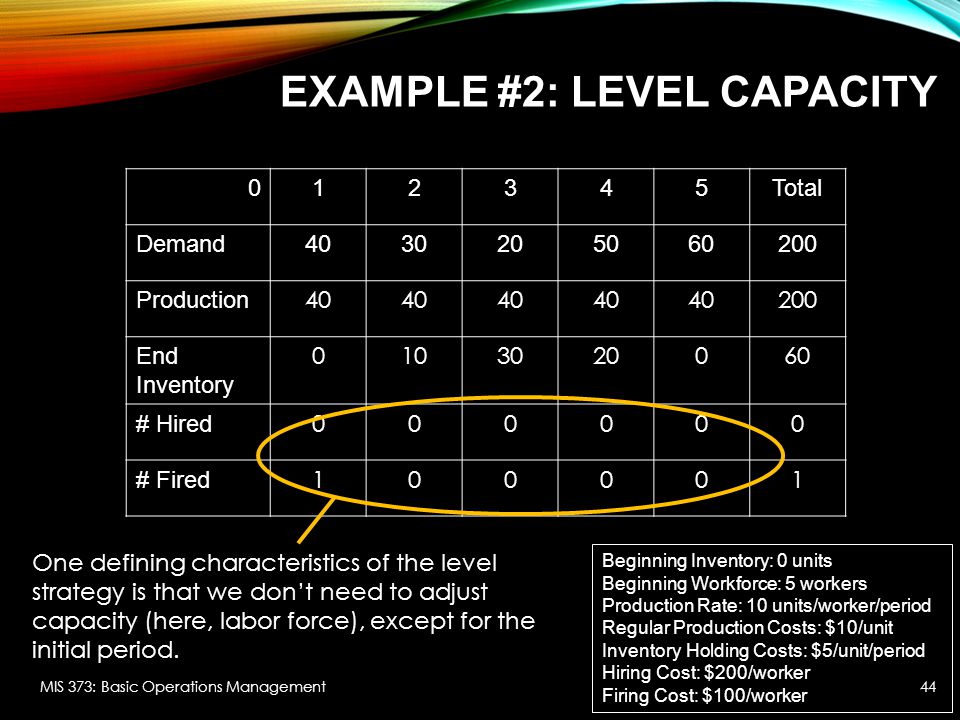



Aggregate Planning Chapter 11 Mis 373 Basic Operations Management Ppt Download



Capacity Planning For Project Managers How To Plan Your Team S Time




The Territorial Impact Of Covid 19 Managing The Crisis Across Levels Of Government




Simulated Capacity 10 Level Vs Snr For Example 1 Picocell Download Scientific Diagram



What Is Aggregate Planning 3 Strategies For Aggregate Production Planning




Itil Capacity Management Bmc Software Blogs



3




Strategy Under Uncertainty




Harnessing The Power Of An Enterprise It Dashboard Uptime Software




Demand And Capacity Management Options Adapted From Fitzsimmons And Download Scientific Diagram




Capacity Planning Types Lead Lag Average Strategies Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




The Territorial Impact Of Covid 19 Managing The Crisis Across Levels Of Government



Operations Strategy Capacity Strategy Ppt Video Online Download



Essentials For Developing And Optimizing A Logical Sourcing Strategy




Fwy5n8yiwwpkum




Strategic Themes Scaled Agile Framework




Solved When Using A Level Capacity Strategy Or Level Chegg Com




Fast Track Strategic Planning For Nonprofits Nonprofit Essentials



Capacity Planning For Project Managers How To Plan Your Team S Time




Capacity Strategy Pdf Economies Of Scale Strategic Management



Level Capacity Plan Level Capacity Plan The Inventory Size Is Varied Keeping The Operation Management




How To Implement Business Capacity Planning Strategies Steps
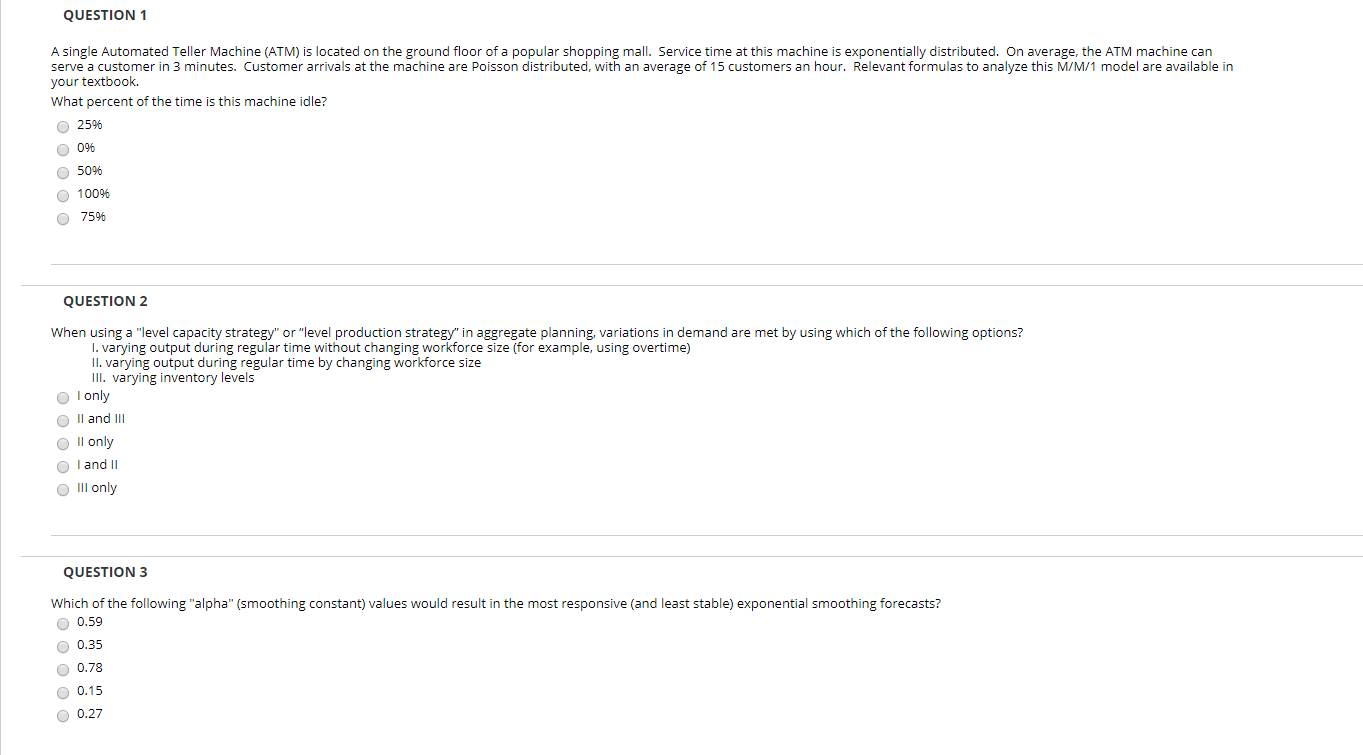



Question 1 A Single Automated Teller Machine Atm Is Chegg Com
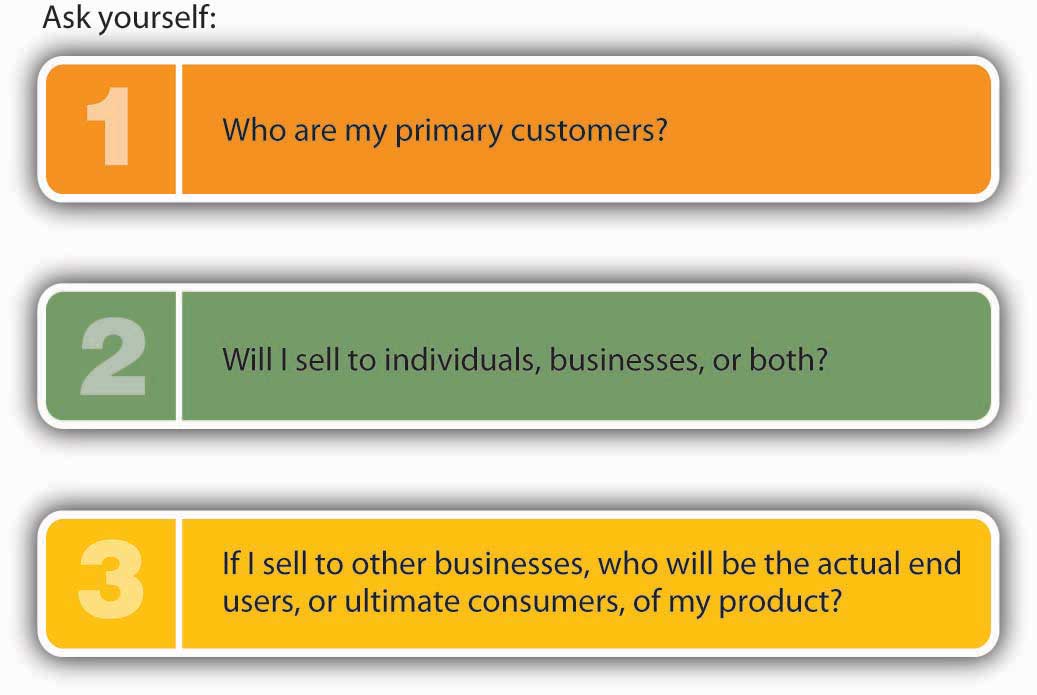



7 1 Capacity Planning Saylor Bus300 Operations Management




04 01 P8 Hybrid Strategy Youtube




Capacity Strategy Pdf Economies Of Scale Strategic Management




Capacity Planning Organization System Examples Definition System Long Term Capacity Planning




Maintenance Capacity Planning Ppt Video Online Download




Anna Deparnay Grunenberg Our Letter To Eu Commission Expresses Our Concerns About Fitfor55 And Euforests We Must Set Ambitious Goals Targets To Reach The Eu S Climate And Biodiversity Goals Eu Has



1




Aggregate Capacity Planning Pdf Free Download



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿